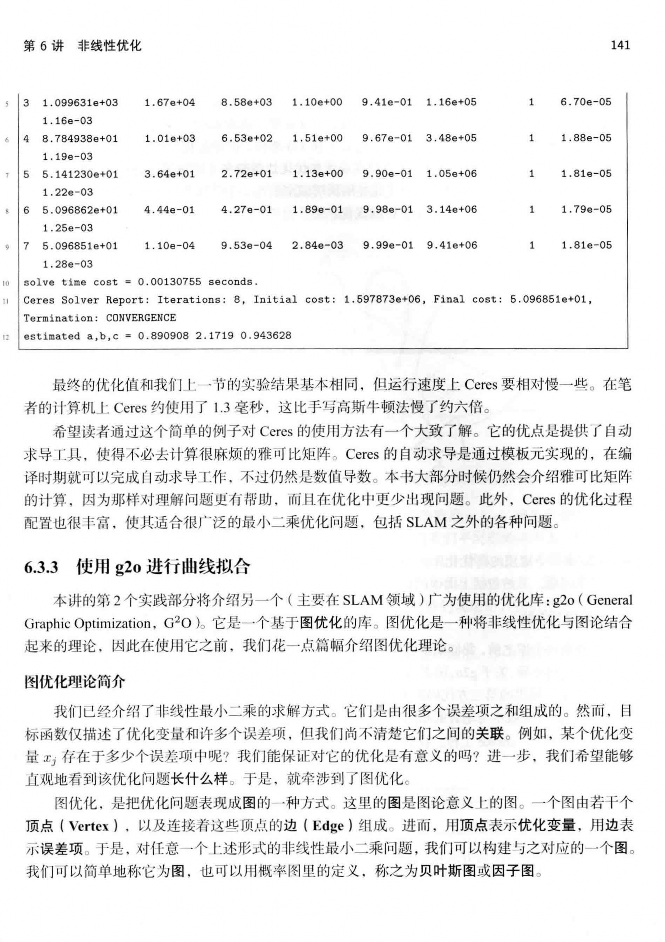
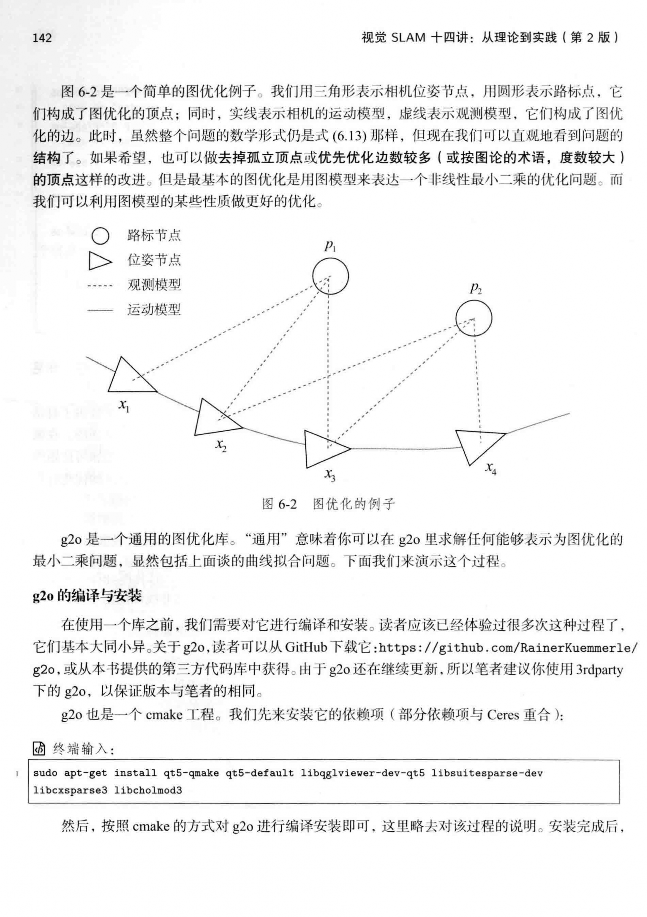
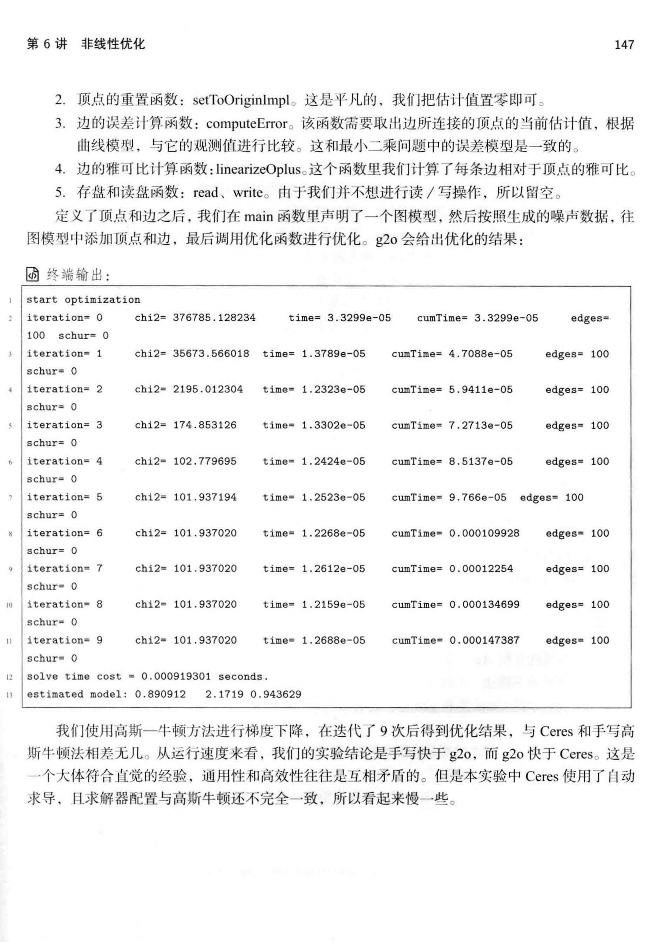
这儿转载书籍《视觉SLAM十四讲从理论到实践 第2版》第6章的内容来学习非线性优化。在理解高斯牛顿法的时候需要注意如下理解。

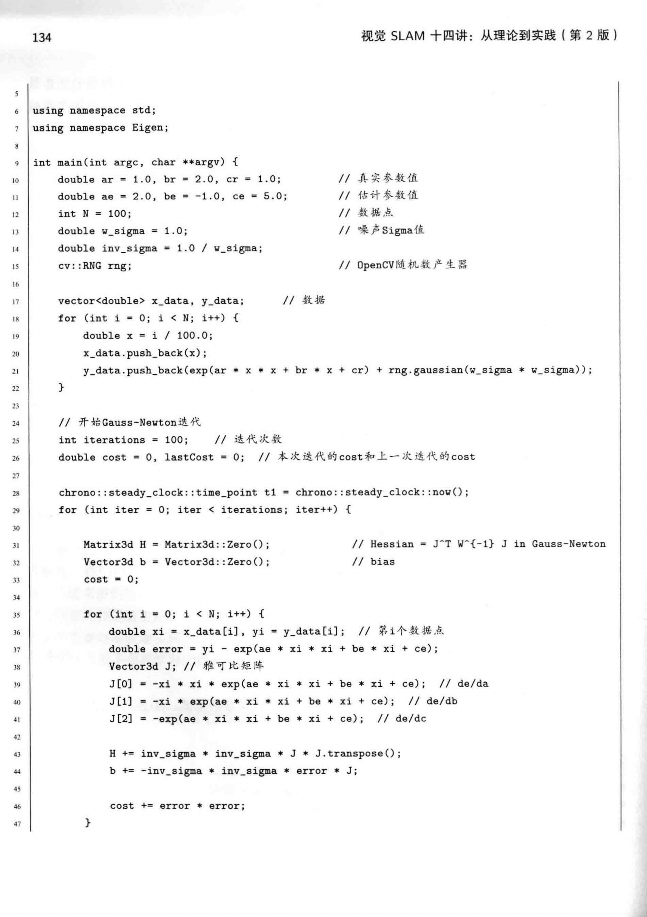
#include <iostream> #include <chrono> #include <Eigen/Core> #include <Eigen/Dense> #include <g2o/stuff/sampler.h> using namespace std; using namespace Eigen; int main(int argc, char **argv) { double ar = 1.0, br = 2.0, cr = 1.0; // 真实参数值 double ae = 2.0, be = -1.0, ce = 5.0; // 估计参数值 int N = 100; // 数据点 double w_sigma = 1.0; // 噪声Sigma值 double inv_sigma = 1.0 / w_sigma; // 大于1的噪声可以让梯度下降慢一些 g2o::Sampler::seedRand(); vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 数据,用于测试的100组数据 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { double x = i / 100.0; x_data.push_back(x); y_data.push_back(exp(ar * x * x + br * x + cr) + g2o::Sampler::gaussRand(0, 0.02)); } // 开始Gauss-Newton迭代 int iterations = 100; // 迭代次数 double cost = 0, lastCost = 0; // 本次迭代的cost和上一次迭代的cost chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) { Matrix3d H = Matrix3d::Zero(); // Hessian = J^T W^{-1} J in Gauss-Newton Vector3d b = Vector3d::Zero(); // bias cost = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { double xi = x_data[i], yi = y_data[i]; // 第i个数据点 double error = yi - exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); Vector3d J; // 雅可比矩阵,fx的一阶导数,注意误差函数的x为向量[a, b, c],和这儿的xi没有关系。 J[0] = -xi * xi * exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/da J[1] = -xi * exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/db J[2] = -exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/dc H += inv_sigma * inv_sigma * J * J.transpose();//海森矩阵H b += -inv_sigma * inv_sigma * error * J;//error为误差函数的值 cost += error * error; } // 求解线性方程 Hx=b,dx为向量[a, b, c],即待优化参数。 Vector3d dx = H.ldlt().solve(b); if (isnan(dx[0])) { cout << "result is nan!" << endl; break; } if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) { cout << "cost: " << cost << ">= last cost: " << lastCost << ", break." << endl; break; } ae += dx[0]; be += dx[1]; ce += dx[2]; lastCost = cost; cout << "total cost: " << cost << ", \t\tupdate: " << dx.transpose() << "\t\testimated params: " << ae << "," << be << "," << ce << endl; } chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now(); chrono::duration</double><double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration</double><double>>(t2 - t1); cout << "solve time cost = " << time_used.count() << " seconds. " << endl; cout << "estimated abc = " << ae << ", " << be << ", " << ce << endl; return 0; } </double></chrono></iostream> |
 本作品采用知识共享署名 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。
本作品采用知识共享署名 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。