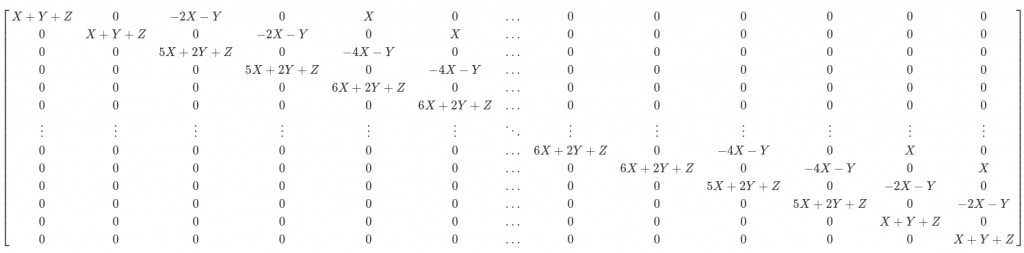原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自慢慢的回味
Apollo的的规划算法基于Frenet坐标系,因此道路中心线的平滑性控制着车辆是否左右频繁晃动,而高精地图的道路中心线往往不够规划。Apollo在/modules/planning/reference_line中包含了多种参考线平滑算法:DiscretePointsReferenceLineSmoother(离散点平滑法,包括FEM_POS_DEVIATION_SMOOTHING有限元位置差异和COS_THETA_SMOOTHING余弦),QpSplineReferenceLineSmoother(三次样条插值法),SpiralReferenceLineSmoother(螺旋曲线法)。本篇以单元测试discrete_points_reference_line_smoother_test.cc的测试TEST_F(DiscretePointsReferenceLineSmootherTest, smooth)为例来分析Apollo对参考线reference line进行离散点平滑(FEM_POS_DEVIATION_SMOOTHING)的原理。
离散点平滑法原理
Apollo默认采用的平滑算法,其将参考线平滑构造成了一个二次优化问题,并使用osqp求解器进行求解。那么通过构建它的代价函数及约束条件就可以利用二次优化框架直接求解。
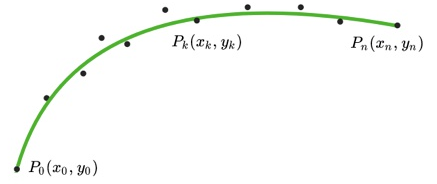
1 首先在参考线上隔相同距离打点(![]() ),绿色的曲线就是算法将要得到的理想曲线。
),绿色的曲线就是算法将要得到的理想曲线。
2 然后列出代价函数:
![]()
其中,![]() 为平滑度代价,
为平滑度代价,![]() 为长度代价,
为长度代价,![]() 为相对原始点偏离代价。
为相对原始点偏离代价。
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ cost_{smooth}=\sum_{k=0}^{n-3}\parallel (x_k+x_{k+2})-2x_{k+1} \parallel^2_2 \]](https://liuxiaofei.com.cn/blog/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f64b22c128dd928b1369191984776b2f_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ cost_{length}=\sum_{k=0}^{n-2}\parallel y_{k+1}-y_k \parallel^2_2 \]](https://liuxiaofei.com.cn/blog/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8a4d80eb5930b977bb9c265eddbd6988_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ cost_{deviation}=\sum_{k=0}^{n-1}\parallel z_k-z_{k-ref} \parallel^2_2 \]](https://liuxiaofei.com.cn/blog/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e5f862bb92e076646dca64ebeb3f6a8d_l3.png)
![]() 要求相邻的3点尽量在同一条直线上,
要求相邻的3点尽量在同一条直线上,![]() 要求相邻2点不能太长,
要求相邻2点不能太长,![]() 要求曲线上的点不能离参考点太远。在FEM_POS_DEVIATION_SMOOTHING算法中,
要求曲线上的点不能离参考点太远。在FEM_POS_DEVIATION_SMOOTHING算法中,![]() 的权重远远大于其它2个。
的权重远远大于其它2个。
3 构建P矩阵:
下面以6个点为例子,展开![]() 得到如下:
得到如下:
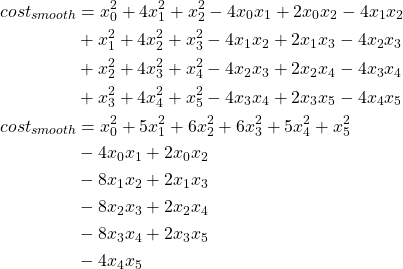
令![]() 为2×2单位矩阵,
为2×2单位矩阵,![]() 表示
表示![]() 。
。
注意到![]() 和
和 ![]() 平分系数得如下矩阵:
平分系数得如下矩阵:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ \begin{bmatrix} X & -2X & X & 0 & 0 & 0\\ -2X & 5X & -4X & X & 0 & 0\\ X & -4X & 6X & -4X & X & 0 \\ 0 & X & -4X & 6X & -4X & X \\ 0 & 0 & X & -4X & 5X & -2X\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & X & -2X & X \end{bmatrix} \]](https://liuxiaofei.com.cn/blog/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-60e712e67d7aa33a832274aa18e3bb47_l3.png)
同理可展开![]() 和
和![]() ,最后取上三角矩阵为:
,最后取上三角矩阵为:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ \begin{bmatrix} X+Y+Z & -2X-Y & X & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 5X+2Y+Z & -4X-Y & X & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 6X+2Y+Z & -4X-Y & X & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 6X+2Y+Z & -4X-Y & X \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 5X+2Y+Z & -2X-Y\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & X+Y+Z \end{bmatrix} \]](https://liuxiaofei.com.cn/blog/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9e90dbc1bebaa1af1ade9837f6ab52f6_l3.png)
离散点平滑法测试用例
TEST_F(DiscretePointsReferenceLineSmootherTest, smooth) { ReferenceLine smoothed_reference_line; EXPECT_DOUBLE_EQ(153.87421245682503, reference_line_->Length()); std::vector<AnchorPoint> anchor_points; const double interval = 10.0; int num_of_anchors = std::max(2, static_cast<int>(reference_line_->Length() / interval + 0.5)); //对reference line按s方向取num_of_anchors个参考点 std::vector<double> anchor_s; common::util::uniform_slice(0.0, reference_line_->Length(), num_of_anchors - 1, &anchor_s); for (const double s : anchor_s) { anchor_points.emplace_back(); auto& last_anchor = anchor_points.back(); auto ref_point = reference_line_->GetReferencePoint(s); last_anchor.path_point = ref_point.ToPathPoint(s); last_anchor.lateral_bound = 0.25; last_anchor.longitudinal_bound = 2.0; } anchor_points.front().longitudinal_bound = 1e-6; anchor_points.front().lateral_bound = 1e-6; anchor_points.back().longitudinal_bound = 1e-6; anchor_points.back().lateral_bound = 1e-6; smoother_->SetAnchorPoints(anchor_points); //调用平滑方法计算平滑参考线 EXPECT_TRUE(smoother_->Smooth(*reference_line_, &smoothed_reference_line)); EXPECT_NEAR(153.0, smoothed_reference_line.Length(), 1.0); } |
离散点平滑方法
bool DiscretePointsReferenceLineSmoother::Smooth( const ReferenceLine& raw_reference_line, ReferenceLine* const smoothed_reference_line) { std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> raw_point2d; std::vector<double> anchorpoints_lateralbound; for (const auto& anchor_point : anchor_points_) { raw_point2d.emplace_back(anchor_point.path_point.x(), anchor_point.path_point.y()); anchorpoints_lateralbound.emplace_back(anchor_point.lateral_bound); } // fix front and back points to avoid end states deviate from the center of // road anchorpoints_lateralbound.front() = 0.0; anchorpoints_lateralbound.back() = 0.0; //归一化参考点 NormalizePoints(&raw_point2d); bool status = false; //默认是FEM_POS_DEVIATION_SMOOTHING方法 const auto& smoothing_method = config_.discrete_points().smoothing_method(); std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> smoothed_point2d; switch (smoothing_method) { case DiscretePointsSmootherConfig::COS_THETA_SMOOTHING: status = CosThetaSmooth(raw_point2d, anchorpoints_lateralbound, &smoothed_point2d); break; case DiscretePointsSmootherConfig::FEM_POS_DEVIATION_SMOOTHING: status = FemPosSmooth(raw_point2d, anchorpoints_lateralbound, &smoothed_point2d); break; default: AERROR << "Smoother type not defined"; return false; } if (!status) { AERROR << "discrete_points reference line smoother fails"; return false; } //反归一化,获取原来的点 DeNormalizePoints(&smoothed_point2d); std::vector<ReferencePoint> ref_points; GenerateRefPointProfile(raw_reference_line, smoothed_point2d, &ref_points); ReferencePoint::RemoveDuplicates(&ref_points); if (ref_points.size() < 2) { AERROR << "Fail to generate smoothed reference line."; return false; } *smoothed_reference_line = ReferenceLine(ref_points); return true; } bool DiscretePointsReferenceLineSmoother::FemPosSmooth( const std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>& raw_point2d, const std::vector<double>& bounds, std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>* ptr_smoothed_point2d) { const auto& fem_pos_config = config_.discrete_points().fem_pos_deviation_smoothing(); //构建FemPosDeviationSmoother FemPosDeviationSmoother smoother(fem_pos_config); // box contraints on pos are used in fem pos smoother, thus shrink the // bounds by 1.0 / sqrt(2.0) std::vector<double> box_bounds = bounds; const double box_ratio = 1.0 / std::sqrt(2.0); for (auto& bound : box_bounds) { bound *= box_ratio; } std::vector<double> opt_x; std::vector<double> opt_y; //调用smoother.Solve求解优化后的opt_x和opt_y bool status = smoother.Solve(raw_point2d, box_bounds, &opt_x, &opt_y); if (!status) { AERROR << "Fem Pos reference line smoothing failed"; return false; } if (opt_x.size() < 2 || opt_y.size() < 2) { AERROR << "Return by fem pos smoother is wrong. Size smaller than 2 "; return false; } CHECK_EQ(opt_x.size(), opt_y.size()) << "x and y result size not equal"; size_t point_size = opt_x.size(); for (size_t i = 0; i < point_size; ++i) { ptr_smoothed_point2d->emplace_back(opt_x[i], opt_y[i]); } return true; } bool FemPosDeviationSmoother::Solve( const std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>& raw_point2d, const std::vector<double>& bounds, std::vector<double>* opt_x, std::vector<double>* opt_y) { if (config_.apply_curvature_constraint()) { if (config_.use_sqp()) { return SqpWithOsqp(raw_point2d, bounds, opt_x, opt_y); } else { return NlpWithIpopt(raw_point2d, bounds, opt_x, opt_y); } } else { //本次测试将调用二次规划框架osqp求解 return QpWithOsqp(raw_point2d, bounds, opt_x, opt_y); } return true; } bool FemPosDeviationSmoother::QpWithOsqp( const std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>& raw_point2d, const std::vector<double>& bounds, std::vector<double>* opt_x, std::vector<double>* opt_y) { if (opt_x == nullptr || opt_y == nullptr) { AERROR << "opt_x or opt_y is nullptr"; return false; } //构造FemPosDeviationOsqpInterface实例 FemPosDeviationOsqpInterface solver; solver.set_weight_fem_pos_deviation(config_.weight_fem_pos_deviation()); solver.set_weight_path_length(config_.weight_path_length()); solver.set_weight_ref_deviation(config_.weight_ref_deviation()); solver.set_max_iter(config_.max_iter()); solver.set_time_limit(config_.time_limit()); solver.set_verbose(config_.verbose()); solver.set_scaled_termination(config_.scaled_termination()); solver.set_warm_start(config_.warm_start()); solver.set_ref_points(raw_point2d); solver.set_bounds_around_refs(bounds); if (!solver.Solve()) { return false; } *opt_x = solver.opt_x(); *opt_y = solver.opt_y(); return true; } |
FemPosDeviationOsqpInterface求解器
bool FemPosDeviationOsqpInterface::Solve() { // Sanity Check ...... // Calculate optimization states definitions //这儿是15个点,其中每个点有x,y方向,所以30个变量,30个约束。 num_of_points_ = static_cast<int>(ref_points_.size()); num_of_variables_ = num_of_points_ * 2; num_of_constraints_ = num_of_variables_; // Calculate kernel //计算二次规划P矩阵,二次项参数 std::vector<c_float> P_data; std::vector<c_int> P_indices; std::vector<c_int> P_indptr; CalculateKernel(&P_data, &P_indices, &P_indptr); // Calculate affine constraints //计算二次规划A矩阵,约束矩阵 std::vector<c_float> A_data; std::vector<c_int> A_indices; std::vector<c_int> A_indptr; std::vector<c_float> lower_bounds; std::vector<c_float> upper_bounds; CalculateAffineConstraint(&A_data, &A_indices, &A_indptr, &lower_bounds, &upper_bounds); // Calculate offset //计算偏移向量q,一次项参数 std::vector<c_float> q; CalculateOffset(&q); // Set primal warm start std::vector<c_float> primal_warm_start; SetPrimalWarmStart(&primal_warm_start); OSQPData* data = reinterpret_cast<OSQPData*>(c_malloc(sizeof(OSQPData))); OSQPSettings* settings = reinterpret_cast<OSQPSettings*>(c_malloc(sizeof(OSQPSettings))); // Define Solver settings osqp_set_default_settings(settings); settings->max_iter = max_iter_; settings->time_limit = time_limit_; settings->verbose = verbose_; settings->scaled_termination = scaled_termination_; settings->warm_start = warm_start_; OSQPWorkspace* work = nullptr; //调用开源框架优化 bool res = OptimizeWithOsqp(num_of_variables_, lower_bounds.size(), &P_data, &P_indices, &P_indptr, &A_data, &A_indices, &A_indptr, &lower_bounds, &upper_bounds, &q, &primal_warm_start, data, &work, settings); if (res == false || work == nullptr || work->solution == nullptr) { AERROR << "Failed to find solution."; // Cleanup osqp_cleanup(work); c_free(data->A); c_free(data->P); c_free(data); c_free(settings); return false; } // Extract primal results x_.resize(num_of_points_); y_.resize(num_of_points_); for (int i = 0; i < num_of_points_; ++i) { int index = i * 2; x_.at(i) = work->solution->x[index]; y_.at(i) = work->solution->x[index + 1]; } // Cleanup ...... return true; } |
P矩阵
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ \begin{bmatrix} X+Y+Z &0 & -2X-Y & 0 & X & 0 & \ldots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & X+Y+Z & 0 & -2X-Y & 0 & X & \ldots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 5X+2Y+Z &0 & -4X-Y & 0 & \ldots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 &0 & 0 &5X+2Y+Z & 0 & -4X-Y & \ldots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 &0 & 0 &0 & 6X+2Y+Z & 0 & \ldots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 &0 & 0 &0 & 0 & 6X+2Y+Z & \ldots & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\ 0 &0 & 0 &0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots& 6X+2Y+Z & 0& -4X-Y & 0 & X & 0 \\ 0 &0 & 0 &0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots& 0 & 6X+2Y+Z& 0 & -4X-Y & 0 & X \\ 0 &0 & 0 &0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots& 0 & 0& 5X+2Y+Z & 0 & -2X-Y & 0 \\ 0 &0 & 0 &0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots& 0 & 0& 0 & 5X+2Y+Z & 0 & -2X-Y \\ 0 &0 & 0 &0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots& 0 & 0& 0 & 0 & X+Y+Z & 0 \\ 0 &0 & 0 &0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots& 0 & 0& 0 & 0 & 0 & X+Y+Z \\ \end{bmatrix} \]](https://liuxiaofei.com.cn/blog/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3ef9da3073132522345d7518d6b33b4f_l3.png)
void FemPosDeviationOsqpInterface::CalculateKernel( std::vector<c_float>* P_data, std::vector<c_int>* P_indices, std::vector<c_int>* P_indptr) { CHECK_GT(num_of_variables_, 4); // Three quadratic penalties are involved: // 1. Penalty x on distance between middle point and point by finite element // estimate; // 2. Penalty y on path length; // 3. Penalty z on difference between points and reference points // General formulation of P matrix is as below(with 6 points as an example): // I is a two by two identity matrix, X, Y, Z represents x * I, y * I, z * I // 0 is a two by two zero matrix // |X+Y+Z, -2X-Y, X, 0, 0, 0 | // |0, 5X+2Y+Z, -4X-Y, X, 0, 0 | // |0, 0, 6X+2Y+Z, -4X-Y, X, 0 | // |0, 0, 0, 6X+2Y+Z, -4X-Y, X | // |0, 0, 0, 0, 5X+2Y+Z, -2X-Y| // |0, 0, 0, 0, 0, X+Y+Z| // Only upper triangle needs to be filled std::vector<std::vector<std::pair<c_int, c_float>>> columns; columns.resize(num_of_variables_); int col_num = 0; for (int col = 0; col < 2; ++col) { columns[col].emplace_back(col, weight_fem_pos_deviation_ + weight_path_length_ + weight_ref_deviation_); ++col_num; } for (int col = 2; col < 4; ++col) { columns[col].emplace_back( col - 2, -2.0 * weight_fem_pos_deviation_ - weight_path_length_); columns[col].emplace_back(col, 5.0 * weight_fem_pos_deviation_ + 2.0 * weight_path_length_ + weight_ref_deviation_); ++col_num; } int second_point_from_last_index = num_of_points_ - 2; for (int point_index = 2; point_index < second_point_from_last_index; ++point_index) { int col_index = point_index * 2; for (int col = 0; col < 2; ++col) { col_index += col; columns[col_index].emplace_back(col_index - 4, weight_fem_pos_deviation_); columns[col_index].emplace_back( col_index - 2, -4.0 * weight_fem_pos_deviation_ - weight_path_length_); columns[col_index].emplace_back( col_index, 6.0 * weight_fem_pos_deviation_ + 2.0 * weight_path_length_ + weight_ref_deviation_); ++col_num; } } int second_point_col_from_last_col = num_of_variables_ - 4; int last_point_col_from_last_col = num_of_variables_ - 2; for (int col = second_point_col_from_last_col; col < last_point_col_from_last_col; ++col) { columns[col].emplace_back(col - 4, weight_fem_pos_deviation_); columns[col].emplace_back( col - 2, -4.0 * weight_fem_pos_deviation_ - weight_path_length_); columns[col].emplace_back(col, 5.0 * weight_fem_pos_deviation_ + 2.0 * weight_path_length_ + weight_ref_deviation_); ++col_num; } for (int col = last_point_col_from_last_col; col < num_of_variables_; ++col) { columns[col].emplace_back(col - 4, weight_fem_pos_deviation_); columns[col].emplace_back( col - 2, -2.0 * weight_fem_pos_deviation_ - weight_path_length_); columns[col].emplace_back(col, weight_fem_pos_deviation_ + weight_path_length_ + weight_ref_deviation_); ++col_num; } CHECK_EQ(col_num, num_of_variables_); int ind_p = 0; for (int i = 0; i < col_num; ++i) { P_indptr->push_back(ind_p); for (const auto& row_data_pair : columns[i]) { // Rescale by 2.0 as the quadratic term in osqp default qp problem setup // is set as (1/2) * x' * P * x P_data->push_back(row_data_pair.second * 2.0); P_indices->push_back(row_data_pair.first); ++ind_p; } } P_indptr->push_back(ind_p); } |
q向量
![]()
q向量
void FemPosDeviationOsqpInterface::CalculateOffset(std::vector<c_float>* q) { for (int i = 0; i < num_of_points_; ++i) { const auto& ref_point_xy = ref_points_[i]; q->push_back(-2.0 * weight_ref_deviation_ * ref_point_xy.first); q->push_back(-2.0 * weight_ref_deviation_ * ref_point_xy.second); } } |
设置限制并使用OSQP优化
void FemPosDeviationOsqpInterface::CalculateAffineConstraint( std::vector<c_float>* A_data, std::vector<c_int>* A_indices, std::vector<c_int>* A_indptr, std::vector<c_float>* lower_bounds, std::vector<c_float>* upper_bounds) { int ind_A = 0; for (int i = 0; i < num_of_variables_; ++i) { A_data->push_back(1.0); A_indices->push_back(i); A_indptr->push_back(ind_A); ++ind_A; } A_indptr->push_back(ind_A); for (int i = 0; i < num_of_points_; ++i) { const auto& ref_point_xy = ref_points_[i]; upper_bounds->push_back(ref_point_xy.first + bounds_around_refs_[i]); upper_bounds->push_back(ref_point_xy.second + bounds_around_refs_[i]); lower_bounds->push_back(ref_point_xy.first - bounds_around_refs_[i]); lower_bounds->push_back(ref_point_xy.second - bounds_around_refs_[i]); } } bool FemPosDeviationOsqpInterface::OptimizeWithOsqp( const size_t kernel_dim, const size_t num_affine_constraint, std::vector<c_float>* P_data, std::vector<c_int>* P_indices, std::vector<c_int>* P_indptr, std::vector<c_float>* A_data, std::vector<c_int>* A_indices, std::vector<c_int>* A_indptr, std::vector<c_float>* lower_bounds, std::vector<c_float>* upper_bounds, std::vector<c_float>* q, std::vector<c_float>* primal_warm_start, OSQPData* data, OSQPWorkspace** work, OSQPSettings* settings) { CHECK_EQ(lower_bounds->size(), upper_bounds->size()); data->n = kernel_dim; data->m = num_affine_constraint; data->P = csc_matrix(data->n, data->n, P_data->size(), P_data->data(), P_indices->data(), P_indptr->data()); data->q = q->data(); data->A = csc_matrix(data->m, data->n, A_data->size(), A_data->data(), A_indices->data(), A_indptr->data()); data->l = lower_bounds->data(); data->u = upper_bounds->data(); *work = osqp_setup(data, settings); // osqp_setup(work, data, settings); osqp_warm_start_x(*work, primal_warm_start->data()); // Solve Problem osqp_solve(*work); auto status = (*work)->info->status_val; if (status < 0) { AERROR << "failed optimization status:\t" << (*work)->info->status; return false; } if (status != 1 && status != 2) { AERROR << "failed optimization status:\t" << (*work)->info->status; return false; } return true; } |
本作品采用知识共享署名 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。