原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自慢慢的回味
本文链接地址: CGAN与GAN的区别
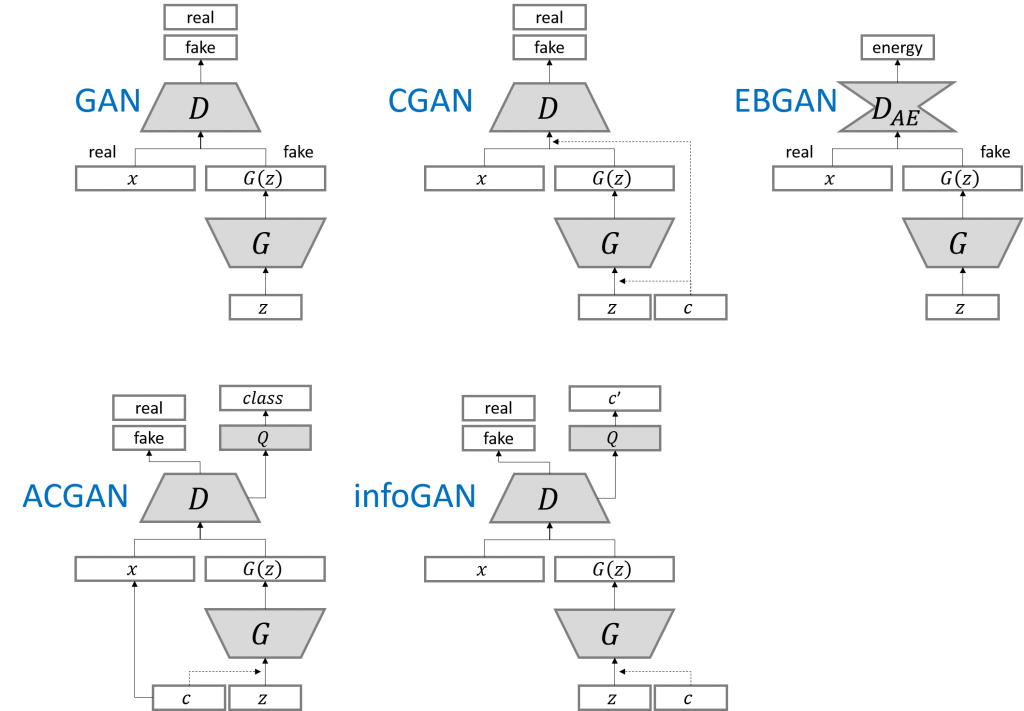
CGAN与GAN的区别如下
GAN视频讲解参考
CGAN视频讲解参考
在生成网络的输入和鉴别网络的输入都混入label,这样生成网络就会学会根据label生成含有label特征的图片;鉴别网络就能学会根据label快速学会分类图片。
如下生成网络model不直接传入noise,而是传入noise和label对于元素相乘的结果。
label[1,]->Embedding[10,100]->label_embedding[1,100]->Flatten[100,] X Noise[100,] = model_input[100,]
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,)) label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32') label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(self.num_classes, self.latent_dim)(label)) model_input = multiply([noise, label_embedding]) img = model(model_input) |
如下鉴别网络model不直接传入img,也是传入img和label对于元素相乘的结果。
label[1,]->Embedding[10,28*28*1]->label_embedding[1,784]->Flatten[784,] X img[28,28,1]->Flaten[784,] = model_input[784,]
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape) label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32') label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(self.num_classes, np.prod(self.img_shape))(label)) flat_img = Flatten()(img) model_input = multiply([flat_img, label_embedding]) img = model(model_input) |
附基于Keras的测试程序
from __future__ import print_function, division from keras.datasets import mnist from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply from keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D from keras.layers.advanced_activations import LeakyReLU from keras.layers.convolutional import UpSampling2D, Conv2D from keras.models import Sequential, Model from keras.optimizers import Adam import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np class CGAN(): def __init__(self): # Input shape self.img_rows = 28 self.img_cols = 28 self.channels = 1 self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels) self.num_classes = 10 self.latent_dim = 100 optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5) # Build and compile the discriminator self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator() self.discriminator.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy'], optimizer=optimizer, metrics=['accuracy']) # Build the generator self.generator = self.build_generator() # The generator takes noise and the target label as input # and generates the corresponding digit of that label noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,)) label = Input(shape=(1,)) img = self.generator([noise, label]) # For the combined model we will only train the generator self.discriminator.trainable = False # The discriminator takes generated image as input and determines validity # and the label of that image valid = self.discriminator([img, label]) # The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator) # Trains generator to fool discriminator self.combined = Model([noise, label], valid) self.combined.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy'], optimizer=optimizer) def build_generator(self): model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.latent_dim)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)) model.add(Dense(512)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)) model.add(Dense(1024)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)) model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh')) model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape)) model.summary() noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,)) label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32') label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(self.num_classes, self.latent_dim)(label)) model_input = multiply([noise, label_embedding]) img = model(model_input) return Model([noise, label], img) def build_discriminator(self): model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(512, input_dim=np.prod(self.img_shape))) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(Dense(512)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(Dropout(0.4)) model.add(Dense(512)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(Dropout(0.4)) model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.summary() img = Input(shape=self.img_shape) label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32') label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(self.num_classes, np.prod(self.img_shape))(label)) flat_img = Flatten()(img) model_input = multiply([flat_img, label_embedding]) validity = model(model_input) return Model([img, label], validity) def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50): # Load the dataset (X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data() # Configure input X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5 X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3) y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1) # Adversarial ground truths valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1)) fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1)) for epoch in range(epochs): # --------------------- # Train Discriminator # --------------------- # Select a random half batch of images idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size) imgs, labels = X_train[idx], y_train[idx] # Sample noise as generator input noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 100)) # Generate a half batch of new images gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, labels]) # Train the discriminator d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([imgs, labels], valid) d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([gen_imgs, labels], fake) d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake) # --------------------- # Train Generator # --------------------- # Condition on labels sampled_labels = np.random.randint(0, 10, batch_size).reshape(-1, 1) # Train the generator g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch([noise, sampled_labels], valid) # Plot the progress print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss)) # If at save interval => save generated image samples if epoch % sample_interval == 0: self.sample_images(epoch) def sample_images(self, epoch): r, c = 2, 5 noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, 100)) sampled_labels = np.arange(0, 10).reshape(-1, 1) gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, sampled_labels]) # Rescale images 0 - 1 gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5 fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c) cnt = 0 for i in range(r): for j in range(c): axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt,:,:,0], cmap='gray') axs[i,j].set_title("Digit: %d" % sampled_labels[cnt]) axs[i,j].axis('off') cnt += 1 fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch) plt.close() if __name__ == '__main__': cgan = CGAN() cgan.train(epochs=20000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200) |
本作品采用知识共享署名 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。