原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自慢慢的回味
本文链接地址: G2O优化解析-自动微分
上文G2O优化解析-手动微分我们学过用G2O来实现拟合曲线,但是大多情况下微分并不好计算,因为我们可能根本就不知道目标函数是什么,而是只知道一些断断续续的约束函数。导数主要以梯度和黑森函数的形式存在于机器学习中,自动微分(AD),也称为算法微分或简称“自动微分”,是一系列技术,类似于反向传播,但比反向传播更为普遍,用于高效、准确地计算以计算机程序表示的数值函数的导数。
接上篇G2O优化解析-手动微分,接着解析G2O框架对非线性优化的实现。
通过自动微分计算雅可比矩阵
什么是自动微分
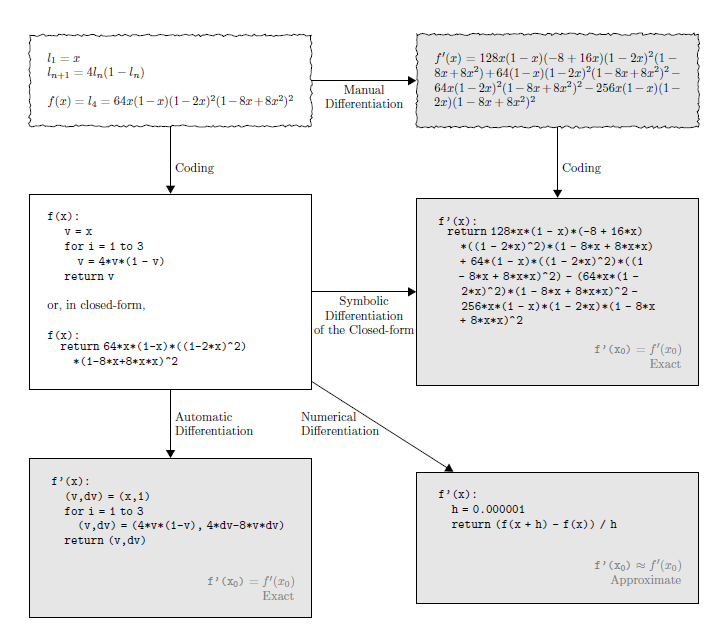
让计算机实现微分功能,有以下四种方式:
1 手工计算出微分,然后编码进代码
2 数值微分 (numerical differentiation)
3 符号微分 (symbolic differentiation)
4 自动微分
下面的图片展示了四种微分方式:
数值微分
分为下面两种方式
前向差分
中心差分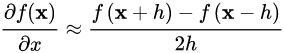
前向差分很少使用,因为前向差分的误差是![]() , 而中心差分的误差是
, 而中心差分的误差是![]() , 中心差分的误差更小。
, 中心差分的误差更小。
数值微分中存在截断误差 (Truncation error)和舍入误差 (Round-off error)。截断误差是对某种数学运算过程进行截断,将函数进行泰勒展开, 我们只可以计算前面几项,而后面的项将被截断。舍入误差是由于计算机使用有限的比特位表示实数时,不能精确表示引起的误差。
自动微分
自动微分是将一个复杂的数学运算过程分解为一系列简单的基本运算,每一项基本运算都可以通过查表得出来。自动微分有两种形式:前向模式和后向模式。
前向模式forward mode
假如我们有如下的多项式,需要计算其微分,可以构建如下的图进行计算:
前向模式的计算方式如下,左列为值的计算,右列为微分的计算。它可以同时进行值和微分的计算。

后向模式backward mode
反向模式的计算方式如下,先通过左列计算值,然后反过来通过右列计算微分。
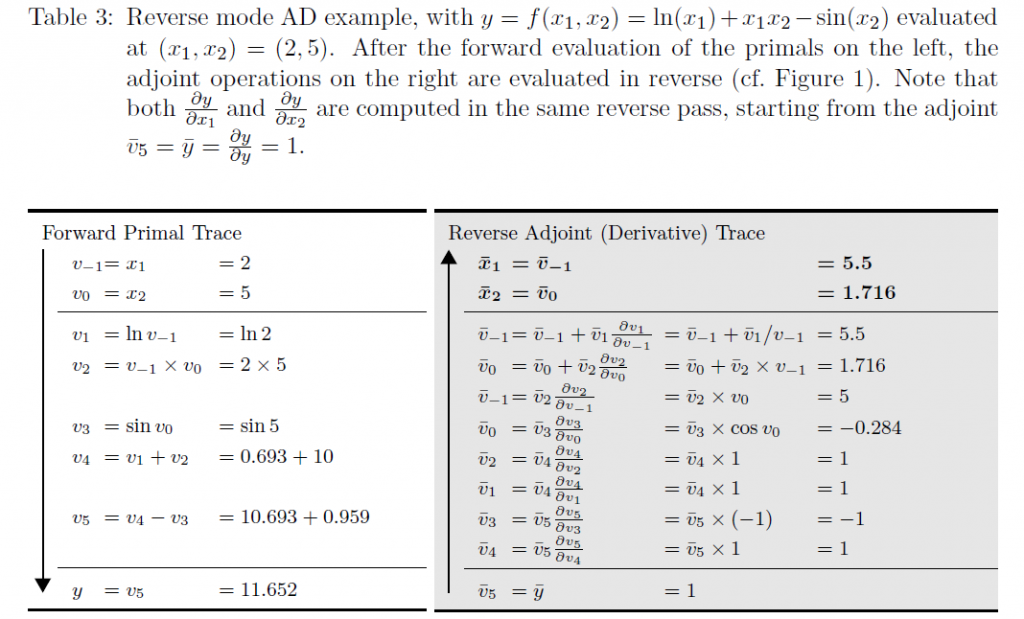
当输出的维度大于输入的时候,适宜使用前向模式微分;当输出维度远远小于输入的时候,适宜使用反向模式微分。
自动微分的原理
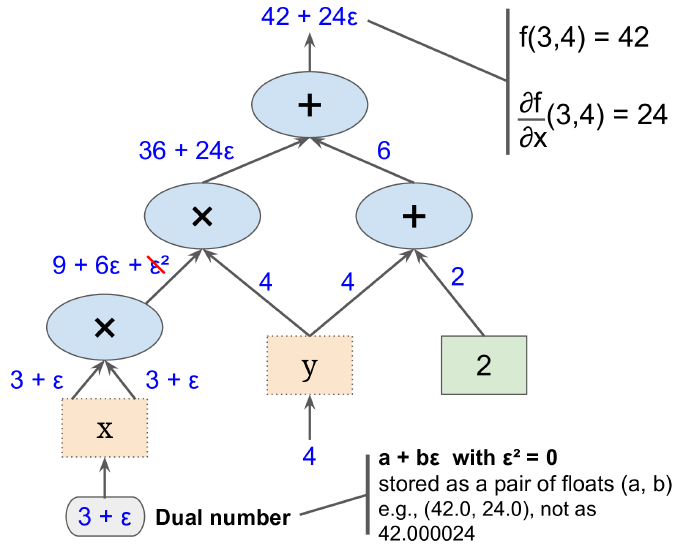
二元数(Dual number)和射流(Jet)
二元数是实数的一个延伸,类似于复数。复数则通过引入虚数来增加实数,比如![]() ,二元数引入了一个极小(infinitesimal)二元数单位,比如
,二元数引入了一个极小(infinitesimal)二元数单位,比如![]() ,且
,且![]() (平方后太小可以忽略)。一个二元数
(平方后太小可以忽略)。一个二元数![]() 包含两个分量,实分量
包含两个分量,实分量![]() 和极小分量的
和极小分量的![]() 。令人惊喜的是,这个简单的变化带来了一种方便的计算精确导数的方法,而不需要复杂的符号表达式。
。令人惊喜的是,这个简单的变化带来了一种方便的计算精确导数的方法,而不需要复杂的符号表达式。
例如,考虑函数
![]()
然后
(1) 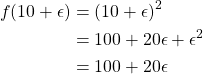
观察![]() 的系数,我们发现
的系数,我们发现![]() 。事实上,这个规律可以推广到不是多项式的函数。考虑一个任意可微函数
。事实上,这个规律可以推广到不是多项式的函数。考虑一个任意可微函数![]() 。然后我们可以计算
。然后我们可以计算![]() ,通过在
,通过在![]() 附近做泰勒展开,这就得到了无穷级数
附近做泰勒展开,这就得到了无穷级数
(2) 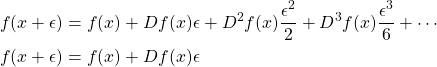
记住,![]() 。
。
射流Jet是一个![]() 维二元数。我们定义
维二元数。我们定义![]() 个极小单位
个极小单位![]() 。并且存在性质
。并且存在性质![]() 。射流数由实数a和n维极小分量组成。
。射流数由实数a和n维极小分量组成。
![]()
为了简化我们改写为这种形式
![]()
然后,使用泰勒级数展开,我们可以看到:
![]()
对多变量函数![]() 相似。对于自变量
相似。对于自变量![]() :
:
![]()
如果每个选取的极小量![]() 是
是![]() 标准基向量,那么上面的表达式就可以简化为
标准基向量,那么上面的表达式就可以简化为
![]()
我们可以通过查找![]() 的系数来提取雅可比矩阵的坐标。
的系数来提取雅可比矩阵的坐标。
实现射流(Jet)
为了让上面学到的内容在实践中发挥作用,我们需要能够计算函数ff的值,不仅在自变量是实数的时候,也需要在自变量是二元数的情况下适用。但是通常我们并非通过泰勒展开式来求函数值。这也就是为什么我们需要用到C++模板和操作符重载。下面的代码段实现了Jet类以及对该类的一些操作和函数。
template<int N> struct Jet { double a; Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, N> v; }; template<int N> Jet<N> operator+(const Jet<N>& f, const Jet<N>& g) { return Jet<N>(f.a + g.a, f.v + g.v); } template<int N> Jet<N> operator-(const Jet<N>& f, const Jet<N>& g) { return Jet<N>(f.a - g.a, f.v - g.v); } template<int N> Jet<N> operator*(const Jet<N>& f, const Jet<N>& g) { return Jet<N>(f.a * g.a, f.a * g.v + f.v * g.a); } template<int N> Jet<N> operator/(const Jet<N>& f, const Jet<N>& g) { return Jet<N>(f.a / g.a, f.v / g.a - f.a * g.v / (g.a * g.a)); } template <int N> Jet<N> exp(const Jet<N>& f) { return Jet<T, N>(exp(f.a), exp(f.a) * f.v); } // This is a simple implementation for illustration purposes, the // actual implementation of pow requires careful handling of a number // of corner cases. template <int N> Jet<N> pow(const Jet<N>& f, const Jet<N>& g) { return Jet<N>(pow(f.a, g.a), g.a * pow(f.a, g.a - 1.0) * f.v + pow(f.a, g.a) * log(f.a); * g.v); } |
有了这些重载的函数,我们现在可以用一个Jets数组来调用Rat43CostFunctor,而不是double双精度类型。将其与初始化的Jets结合起来,我们就可以计算雅可比矩阵了:
struct Rat43CostFunctor { Rat43CostFunctor(const double x, const double y) : x_(x), y_(y) {} template <typename T> bool operator()(const T* parameters, T* residuals) const { const T b1 = parameters[0]; const T b2 = parameters[1]; const T b3 = parameters[2]; const T b4 = parameters[3]; //这儿的运算就是Jet的运算,在计算值的同时也计算出了雅可比矩阵 residuals[0] = b1 * pow(1.0 + exp(b2 - b3 * x_), -1.0 / b4) - y_; return true; } private: const double x_; const double y_; }; CostFunction* cost_function = new AutoDiffCostFunction<Rat43CostFunctor, 1, 4>( new Rat43CostFunctor(x, y)); class Rat43Automatic : public ceres::SizedCostFunction<1,4> { public: Rat43Automatic(const Rat43CostFunctor* functor) : functor_(functor) {} virtual ~Rat43Automatic() {} virtual bool Evaluate(double const* const* parameters, double* residuals, double** jacobians) const { // Just evaluate the residuals if Jacobians are not required. if (!jacobians) return (*functor_)(parameters[0], residuals); // Initialize the Jets ceres::Jet<4> jets[4]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { jets[i].a = parameters[0][i]; jets[i].v.setZero(); jets[i].v[i] = 1.0; } ceres::Jet<4> result; (*functor_)(jets, &result); // Copy the values out of the Jet. residuals[0] = result.a; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { jacobians[0][i] = result.v[i]; } return true; } private: std::unique_ptr<const Rat43CostFunctor> functor_; }; |
这就是AutoDiffCostFunction的核心工作原理。
自动微分解析例程
// g2o - General Graph Optimization // Copyright (C) 2012 R. Kümmerle // All rights reserved. // // Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without // modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are // met: // // * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, // this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. // * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright // notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the // documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. // // THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS // IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED // TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A // PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT // HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, // SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED // TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR // PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF // LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING // NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS // SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. #include <Eigen/Core> #include <Eigen/Geometry> #include <iostream> #include "g2o/core/auto_differentiation.h" #include "g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h" #include "g2o/core/base_vertex.h" #include "g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_factory.h" #include "g2o/core/sparse_optimizer.h" #include "g2o/stuff/command_args.h" #include "g2o/stuff/sampler.h" using namespace std; G2O_USE_OPTIMIZATION_LIBRARY(dense); double errorOfSolution(int numPoints, Eigen::Vector2d* points, const Eigen::Vector3d& circle) { Eigen::Vector2d center = circle.head<2>(); double radius = circle(2); double error = 0.; for (int i = 0; i < numPoints; ++i) { double d = (points[i] - center).norm() - radius; error += d * d; } return error; } /** * \brief a circle located at x,y with radius r */ class VertexCircle : public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Eigen::Vector3d> { public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW; VertexCircle() {} virtual bool read(std::istream& /*is*/) { return false; } virtual bool write(std::ostream& /*os*/) const { return false; } virtual void setToOriginImpl() { cerr << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << " not implemented yet" << endl; } virtual void oplusImpl(const double* update) { Eigen::Vector3d::ConstMapType v(update); _estimate += v; } }; /** * \brief measurement for a point on the circle * * Here the measurement is the point which is on the circle. * The error function computes the distance of the point to * the center minus the radius of the circle. */ class EdgePointOnCircle : public g2o::BaseUnaryEdge<1, Eigen::Vector2d, VertexCircle> { public: EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW EdgePointOnCircle() {} virtual bool read(std::istream& /*is*/) { return false; } virtual bool write(std::ostream& /*os*/) const { return false; } //构建一个自动微分计算的cost函数,下面的g2o::AutoDifferentiation::linearize(this)会调用此方法进行微分计算 template <typename T> bool operator()(const T* circle, T* error) const { typename g2o::VectorN<2, T>::ConstMapType center(circle); const T& radius = circle[2]; //误差为 测量的圆心到预测参数的圆心的距离 与 预测参数半径 的差值。 error[0] = (measurement().cast<T>() - center).norm() - radius; return true; } //展开后为: // void computeError() { \ // g2o::AutoDifferentiation<std::remove_reference<decltype(*this)>::type>::computeError(this); \ // } \ // void linearizeOplus() { \ // g2o::AutoDifferentiation<std::remove_reference<decltype(*this)>::type>::linearize(this); \ // } G2O_MAKE_AUTO_AD_FUNCTIONS // use autodiff }; int main(int argc, char** argv) { int numPoints; int maxIterations; bool verbose; g2o::CommandArgs arg; arg.param("numPoints", numPoints, 100, "number of points sampled from the circle"); arg.param("i", maxIterations, 10, "perform n iterations"); arg.param("v", verbose, false, "verbose output of the optimization process"); arg.parseArgs(argc, argv); // generate random data //用圆心(4,2)和半径2生成在圆上的100个点。 Eigen::Vector2d center(4.0, 2.0); double radius = 2.0; Eigen::Vector2d* points = new Eigen::Vector2d[numPoints]; g2o::Sampler::seedRand(); for (int i = 0; i < numPoints; ++i) { double r = g2o::Sampler::gaussRand(radius, 0.05); double angle = g2o::Sampler::uniformRand(0.0, 2.0 * M_PI); points[i].x() = center.x() + r * cos(angle); points[i].y() = center.y() + r * sin(angle); } // setup the solver g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; optimizer.setVerbose(false); // allocate the solver g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmProperty solverProperty; optimizer.setAlgorithm( g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmFactory::instance()->construct("lm_dense", solverProperty)); // build the optimization problem given the points // 1. add the circle vertex VertexCircle* circle = new VertexCircle(); circle->setId(0); //初始化的参数圆心(3,3),半径3 //根据上面的100个点和初始参数优化估计出最终合理的圆心和半径 circle->setEstimate(Eigen::Vector3d(3.0, 3.0, 3.0)); // some initial value for the circle optimizer.addVertex(circle); // 2. add the points we measured for (int i = 0; i < numPoints; ++i) { EdgePointOnCircle* e = new EdgePointOnCircle; e->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double, 1, 1>::Identity()); e->setVertex(0, circle); e->setMeasurement(points[i]); optimizer.addEdge(e); } // perform the optimization optimizer.initializeOptimization(); optimizer.setVerbose(verbose); optimizer.optimize(maxIterations); if (verbose) cout << endl; // print out the result cout << "Iterative least squares solution" << endl; cout << "center of the circle " << circle->estimate().head<2>().transpose() << endl; cout << "radius of the cirlce " << circle->estimate()(2) << endl; cout << "error " << errorOfSolution(numPoints, points, circle->estimate()) << endl; cout << endl; // solve by linear least squares // Let (a, b) be the center of the circle and r the radius of the circle. // For a point (x, y) on the circle we have: // (x - a)^2 + (y - b)^2 = r^2 // This leads to // (-2x -2y 1)^T * (a b c) = -x^2 - y^2 (1) // where c = a^2 + b^2 - r^2. // Since we have a bunch of points, we accumulate Eqn (1) in a matrix and // compute the normal equation to obtain a solution for (a b c). // Afterwards the radius r is recovered. Eigen::MatrixXd A(numPoints, 3); Eigen::VectorXd b(numPoints); for (int i = 0; i < numPoints; ++i) { A(i, 0) = -2 * points[i].x(); A(i, 1) = -2 * points[i].y(); A(i, 2) = 1; b(i) = -pow(points[i].x(), 2) - pow(points[i].y(), 2); } Eigen::Vector3d solution = (A.transpose() * A).ldlt().solve(A.transpose() * b); // calculate the radius of the circle given the solution so far solution(2) = sqrt(pow(solution(0), 2) + pow(solution(1), 2) - solution(2)); cout << "Linear least squares solution" << endl; cout << "center of the circle " << solution.head<2>().transpose() << endl; cout << "radius of the cirlce " << solution(2) << endl; cout << "error " << errorOfSolution(numPoints, points, solution) << endl; // clean up delete[] points; return 0; } |
自动微分的调用
相比上面的手动计算雅可比方式CurveFittingEdge::linearizeOplus,这儿会用ceres::internal::AutoDifferentiate<1, ceres::internal::ParameterDims
g2o::BaseFixedSizedEdge<1, Eigen::Matrix
-> g2o::AutoDifferentiation
-> EdgePointOnCircle::linearizeOplus() at circle_fit.cpp:97
-> g2o::AutoDifferentiation
-> ceres::internal::AutoDifferentiate<1, ceres::internal::ParameterDims
//文件auto_differentiation.h的代码 template <typename Edge, typename EstimateAccess = EstimateAccessor<Edge>> class AutoDifferentiation { ...... /** * Linearize (compute the Jacobians) for the given edge. * Stores the Jacobians in the members of the edge. * A vertex that is fixed will obtain a Jacobian with all elements set to zero. * In the particular case that all vertices are fixed, we terminate early and do not start * evaluation of the Jacobian. */ static void linearize(Edge* that) { static_assert(Edge::Dimension > 0, "Dynamically sized edges are not supported"); linearizeOplusNs(that, std::make_index_sequence<Edge::_nr_of_vertices>()); } //that为边,误差项。 Ints为序列类型模板。 template <std::size_t... Ints> static void linearizeOplusNs(Edge* that, std::index_sequence<Ints...>) { static_assert(std::min({Edge::template VertexXnType<Ints>::Dimension...}) > 0, "Dynamically sized vertices are not supported"); // all vertices are fixed, no need to compute anything here if (that->allVerticesFixed()) { int unused[] = {(that->template jacobianOplusXn<Ints>().setZero(), 0)...}; (void)unused; return; } // tuple containing the Jacobians std::tuple<ADJacobianType<Edge::Dimension, Edge::template VertexXnType<Ints>::Dimension>...> ad_jacobians; // setting up the pointer to the parameters and the Jacobians for calling AD. //获取Edge里面的顶点参数项 EstimateAccess estimateAccess; number_t* parameters[] = {estimateAccess.template data<Ints>(that)...}; // number_t* parameters[] = { /* trivial case would be */ // const_cast<number_t*>(that->template vertexXn<Ints>()->estimate().data())...}; // pointers to the Jacobians, set to NULL if vertex is fixed to skip computation number_t* jacobians[] = {that->template vertexXn<Ints>()->fixed() ? nullptr : const_cast<number_t*>(std::get<Ints>(ad_jacobians).data())...}; // Calls the automatic differentiation for evaluation of the Jacobians. number_t errorValue[Edge::Dimension]; using AutoDiffDims = ceres::internal::StaticParameterDims<Edge::template VertexXnType<Ints>::Dimension...>; //参数依次为边EdgePointOnCircle实例,参数,输出维数,误差函数值,雅可比矩阵 bool diffState = ceres::internal::AutoDifferentiate<Edge::Dimension, AutoDiffDims, Edge, number_t>( *that, parameters, Edge::Dimension, errorValue, jacobians); assert(diffState && "Error during Automatic Differentiation"); if (!diffState) { // something went wrong during AD int unused[] = {(std::get<Ints>(ad_jacobians).setZero(), 0)...}; (void)unused; return; } // copy over the Jacobians (convert row-major -> column-major) for non-fixed vertices //复制计算出的雅可比矩阵到顶点的雅可比参数矩阵上 int unused[] = { that->template vertexXn<Ints>()->fixed() ? (that->template jacobianOplusXn<Ints>().setZero(), 0) : (assign(that->template jacobianOplusXn<Ints>(), std::get<Ints>(ad_jacobians)), 0)...}; (void)unused; } |
//文件autodiff.h的代码,从此方法开始调用ceres的自动微分方法 template <int kNumResiduals, typename ParameterDims, typename Functor, typename T> inline bool AutoDifferentiate(const Functor& functor, T const* const* parameters, int dynamic_num_outputs, T* function_value, T** jacobians) { typedef Jet<T, ParameterDims::kNumParameters> JetT; using Parameters = typename ParameterDims::Parameters; ArraySelector<JetT, ParameterDims::kNumParameters, CERES_AUTODIFF_MAX_PARAMETERS_ON_STACK> parameters_as_jets(ParameterDims::kNumParameters); // Pointers to the beginning of each parameter block std::array<JetT*, ParameterDims::kNumParameterBlocks> unpacked_parameters = ParameterDims::GetUnpackedParameters(parameters_as_jets.data()); // If the number of residuals is fixed, we use the template argument as the // number of outputs. Otherwise we use the num_outputs parameter. Note: The // ?-operator here is compile-time evaluated, therefore num_outputs is also // a compile-time constant for functors with fixed residuals. const int num_outputs = kNumResiduals == DYNAMIC ? dynamic_num_outputs : kNumResiduals; ArraySelector<JetT, kNumResiduals, CERES_AUTODIFF_MAX_RESIDUALS_ON_STACK> residuals_as_jets(num_outputs); // Invalidate the output Jets, so that we can detect if the user // did not assign values to all of them. //残差的双数表示。 for (int i = 0; i < num_outputs; ++i) { residuals_as_jets[i].a = kImpossibleValue; residuals_as_jets[i].v.setConstant(kImpossibleValue); } //复制现有的参数到parameters_as_jets Make1stOrderPerturbations<Parameters>::Apply(parameters, parameters_as_jets.data()); //这儿最终会调用EdgePointOnCircle::operator()<ceres::Jet<double, 3> > at circle_fit.cpp:91得到微分计算结果 if (!VariadicEvaluate<ParameterDims>( functor, unpacked_parameters.data(), residuals_as_jets.data())) { return false; } //复制计算的值结果到function_value,微分结果到jacobians Take0thOrderPart(num_outputs, residuals_as_jets.data(), function_value); Take1stOrderParts<Parameters>::Apply( num_outputs, residuals_as_jets.data(), jacobians); return true; } |
本作品采用知识共享署名 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。