原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自慢慢的回味
本文链接地址: 同时定位与制图-SlamGMapping
机器人如小车如果需要在一个陌生的环境中导航,一个首要的前提就是得由一个地图。这个地图就需要小车利用自己的传感器来制作,这儿一般使用里程计和激光雷达,依赖一定的算法就可以完成。这儿以同时定位与制图-SlamGMapping为例解读。
节点的启动
class SlamGMappingNodelet : public nodelet::Nodelet { public: SlamGMappingNodelet() {} ~SlamGMappingNodelet() {} virtual void onInit() { NODELET_INFO_STREAM("Initialising Slam GMapping nodelet..."); sg_.reset(new SlamGMapping(getNodeHandle(), getPrivateNodeHandle())); NODELET_INFO_STREAM("Starting live SLAM..."); //节点启动 sg_->startLiveSlam(); } private: boost::shared_ptr<SlamGMapping> sg_; }; void SlamGMapping::startLiveSlam() { entropy_publisher_ = private_nh_.advertise<std_msgs::Float64>("entropy", 1, true); sst_ = node_.advertise<nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid>("map", 1, true); sstm_ = node_.advertise<nav_msgs::MapMetaData>("map_metadata", 1, true); ss_ = node_.advertiseService("dynamic_map", &SlamGMapping::mapCallback, this); scan_filter_sub_ = new message_filters::Subscriber<sensor_msgs::LaserScan>(node_, "scan", 5); scan_filter_ = new tf::MessageFilter<sensor_msgs::LaserScan>(*scan_filter_sub_, tf_, odom_frame_, 5); //注册一个回调函数,每收到“scan”消息就调用“laserCallback”函数处理 scan_filter_->registerCallback(boost::bind(&SlamGMapping::laserCallback, this, _1)); transform_thread_ = new boost::thread(boost::bind(&SlamGMapping::publishLoop, this, transform_publish_period_)); } void SlamGMapping::laserCallback(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan::ConstPtr& scan) { laser_count_++; //限流,每throttle_scans_次扫描才处理一次 if ((laser_count_ % throttle_scans_) != 0) return; static ros::Time last_map_update(0,0); //第一次扫描需要初始化Mapper // We can't initialize the mapper until we've got the first scan if(!got_first_scan_) { if(!initMapper(*scan)) return; got_first_scan_ = true; } GMapping::OrientedPoint odom_pose; //传入激光扫描数据和里程计位置,添加一次扫描 if(addScan(*scan, odom_pose)) { ROS_DEBUG("scan processed"); //取最优的粒子位置作为雷达位置 GMapping::OrientedPoint mpose = gsp_->getParticles()[gsp_->getBestParticleIndex()].pose; ROS_DEBUG("new best pose: %.3f %.3f %.3f", mpose.x, mpose.y, mpose.theta); ROS_DEBUG("odom pose: %.3f %.3f %.3f", odom_pose.x, odom_pose.y, odom_pose.theta); ROS_DEBUG("correction: %.3f %.3f %.3f", mpose.x - odom_pose.x, mpose.y - odom_pose.y, mpose.theta - odom_pose.theta); tf::Transform laser_to_map = tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0, 0, mpose.theta), tf::Vector3(mpose.x, mpose.y, 0.0)).inverse(); tf::Transform odom_to_laser = tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0, 0, odom_pose.theta), tf::Vector3(odom_pose.x, odom_pose.y, 0.0)); map_to_odom_mutex_.lock(); map_to_odom_ = (odom_to_laser * laser_to_map).inverse(); map_to_odom_mutex_.unlock(); //大于地图更新周期就更新地图 if(!got_map_ || (scan->header.stamp - last_map_update) > map_update_interval_) { updateMap(*scan); last_map_update = scan->header.stamp; ROS_DEBUG("Updated the map"); } } else ROS_DEBUG("cannot process scan"); } |
初始化Mapper
bool SlamGMapping::initMapper(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan& scan) { laser_frame_ = scan.header.frame_id; // Get the laser's pose, relative to base. tf::Stamped<tf::Pose> ident; tf::Stamped<tf::Transform> laser_pose; ident.setIdentity(); ident.frame_id_ = laser_frame_; ident.stamp_ = scan.header.stamp; try { //获取激光雷达相对小车的真实位置,这才是所有雷达信号的0点 tf_.transformPose(base_frame_, ident, laser_pose); } catch(tf::TransformException e) { ROS_WARN("Failed to compute laser pose, aborting initialization (%s)", e.what()); return false; } //获取雷达上方1米的坐标,用于判断雷达是否安装在小车上 // create a point 1m above the laser position and transform it into the laser-frame tf::Vector3 v; v.setValue(0, 0, 1 + laser_pose.getOrigin().z()); tf::Stamped<tf::Vector3> up(v, scan.header.stamp, base_frame_); try { tf_.transformPoint(laser_frame_, up, up); ROS_DEBUG("Z-Axis in sensor frame: %.3f", up.z()); } catch(tf::TransformException& e) { ROS_WARN("Unable to determine orientation of laser: %s", e.what()); return false; } // gmapping doesnt take roll or pitch into account. So check for correct sensor alignment. if (fabs(fabs(up.z()) - 1) > 0.001) { ROS_WARN("Laser has to be mounted planar! Z-coordinate has to be 1 or -1, but gave: %.5f", up.z()); return false; } //扫描激光束数量 gsp_laser_beam_count_ = scan.ranges.size(); //扫描激光束的中间角度 double angle_center = (scan.angle_min + scan.angle_max)/2; if (up.z() > 0) { //雷达正着装的时候,如果小角大于大角,说明扫描顺序是反的。 do_reverse_range_ = scan.angle_min > scan.angle_max; centered_laser_pose_ = tf::Stamped<tf::Pose>(tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0,0,angle_center), tf::Vector3(0,0,0)), ros::Time::now(), laser_frame_); ROS_INFO("Laser is mounted upwards."); } else { //雷达倒着装的时候,如果小角小于大角,说明扫描顺序是反的。 do_reverse_range_ = scan.angle_min < scan.angle_max; centered_laser_pose_ = tf::Stamped<tf::Pose>(tf::Transform(tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(M_PI,0,-angle_center), tf::Vector3(0,0,0)), ros::Time::now(), laser_frame_); ROS_INFO("Laser is mounted upside down."); } //扫描角的数量就是激光束的数量。循环得到所有激光束对应的角度laser_angles_ // Compute the angles of the laser from -x to x, basically symmetric and in increasing order laser_angles_.resize(scan.ranges.size()); // Make sure angles are started so that they are centered double theta = - std::fabs(scan.angle_min - scan.angle_max)/2; for(unsigned int i=0; i<scan.ranges.size(); ++i) { laser_angles_[i]=theta; theta += std::fabs(scan.angle_increment); } ROS_DEBUG("Laser angles in laser-frame: min: %.3f max: %.3f inc: %.3f", scan.angle_min, scan.angle_max, scan.angle_increment); ROS_DEBUG("Laser angles in top-down centered laser-frame: min: %.3f max: %.3f inc: %.3f", laser_angles_.front(), laser_angles_.back(), std::fabs(scan.angle_increment)); GMapping::OrientedPoint gmap_pose(0, 0, 0); // setting maxRange and maxUrange here so we can set a reasonable default ros::NodeHandle private_nh_("~"); if(!private_nh_.getParam("maxRange", maxRange_)) maxRange_ = scan.range_max - 0.01; if(!private_nh_.getParam("maxUrange", maxUrange_)) maxUrange_ = maxRange_; //实例化激光束处理器 // The laser must be called "FLASER". // We pass in the absolute value of the computed angle increment, on the // assumption that GMapping requires a positive angle increment. If the // actual increment is negative, we'll swap the order of ranges before // feeding each scan to GMapping. gsp_laser_ = new GMapping::RangeSensor("FLASER", gsp_laser_beam_count_, fabs(scan.angle_increment), gmap_pose, 0.0, maxRange_); ROS_ASSERT(gsp_laser_); GMapping::SensorMap smap; smap.insert(make_pair(gsp_laser_->getName(), gsp_laser_)); gsp_->setSensorMap(smap); gsp_odom_ = new GMapping::OdometrySensor(odom_frame_); ROS_ASSERT(gsp_odom_); //从里程计获取激光初始位置 /// @todo Expose setting an initial pose GMapping::OrientedPoint initialPose; if(!getOdomPose(initialPose, scan.header.stamp)) { ROS_WARN("Unable to determine inital pose of laser! Starting point will be set to zero."); initialPose = GMapping::OrientedPoint(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); } gsp_->setMatchingParameters(maxUrange_, maxRange_, sigma_, kernelSize_, lstep_, astep_, iterations_, lsigma_, ogain_, lskip_); //设置运动模型参数 gsp_->setMotionModelParameters(srr_, srt_, str_, stt_); gsp_->setUpdateDistances(linearUpdate_, angularUpdate_, resampleThreshold_); gsp_->setUpdatePeriod(temporalUpdate_); gsp_->setgenerateMap(false); gsp_->GridSlamProcessor::init(particles_, xmin_, ymin_, xmax_, ymax_, delta_, initialPose); gsp_->setllsamplerange(llsamplerange_); gsp_->setllsamplestep(llsamplestep_); /// @todo Check these calls; in the gmapping gui, they use /// llsamplestep and llsamplerange intead of lasamplestep and /// lasamplerange. It was probably a typo, but who knows. gsp_->setlasamplerange(lasamplerange_); gsp_->setlasamplestep(lasamplestep_); gsp_->setminimumScore(minimum_score_); // Call the sampling function once to set the seed. GMapping::sampleGaussian(1,seed_); ROS_INFO("Initialization complete"); return true; } |
处理一次扫描
SlamGMapping::laserCallback() at slam_gmapping.cpp:628
–> SlamGMapping::addScan() at slam_gmapping.cpp:606
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::processScan() at gridslamprocessor.cpp:419
bool SlamGMapping::addScan(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan& scan, GMapping::OrientedPoint& gmap_pose) { //获取里程计位置 if(!getOdomPose(gmap_pose, scan.header.stamp)) return false; if(scan.ranges.size() != gsp_laser_beam_count_) return false; // GMapping wants an array of doubles... double* ranges_double = new double[scan.ranges.size()]; // If the angle increment is negative, we have to invert the order of the readings. if (do_reverse_range_) { ROS_DEBUG("Inverting scan"); int num_ranges = scan.ranges.size(); for(int i=0; i < num_ranges; i++) { // Must filter out short readings, because the mapper won't if(scan.ranges[num_ranges - i - 1] < scan.range_min) ranges_double[i] = (double)scan.range_max; else ranges_double[i] = (double)scan.ranges[num_ranges - i - 1]; } } else { for(unsigned int i=0; i < scan.ranges.size(); i++) { //距离太近的探测改成无限远,因为不可能小于雷达的最小探测距离 // Must filter out short readings, because the mapper won't if(scan.ranges[i] < scan.range_min) ranges_double[i] = (double)scan.range_max; else ranges_double[i] = (double)scan.ranges[i]; } } //把数据存储成RangeReading类型 GMapping::RangeReading reading(scan.ranges.size(), ranges_double, gsp_laser_, scan.header.stamp.toSec()); // ...but it deep copies them in RangeReading constructor, so we don't // need to keep our array around. delete[] ranges_double; reading.setPose(gmap_pose); /* ROS_DEBUG("scanpose (%.3f): %.3f %.3f %.3f\n", scan.header.stamp.toSec(), gmap_pose.x, gmap_pose.y, gmap_pose.theta); */ ROS_DEBUG("processing scan"); //处理这次扫描 return gsp_->processScan(reading); } bool GridSlamProcessor::processScan(const RangeReading & reading, int adaptParticles){ /**retireve the position from the reading, and compute the odometry*/ OrientedPoint relPose=reading.getPose(); if (!m_count){ //第一次的时候,最后位置,上次位置都为这次传入的位置 m_lastPartPose=m_odoPose=relPose; } //write the state of the reading and update all the particles using the motion model for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){ OrientedPoint& pose(it->pose); //根据里程计位置和运动模型,更新当前粒子位置 pose=m_motionModel.drawFromMotion(it->pose, relPose, m_odoPose); } ...... //invoke the callback onOdometryUpdate(); // accumulate the robot translation and rotation OrientedPoint move=relPose-m_odoPose; move.theta=atan2(sin(move.theta), cos(move.theta)); m_linearDistance+=sqrt(move*move); m_angularDistance+=fabs(move.theta); //运动距离不能超过阈值,否则就是错误的 // if the robot jumps throw a warning if (m_linearDistance>m_distanceThresholdCheck){ cerr << "***********************************************************************" << endl; cerr << "********** Error: m_distanceThresholdCheck overridden!!!! *************" << endl; cerr << "m_distanceThresholdCheck=" << m_distanceThresholdCheck << endl; cerr << "Old Odometry Pose= " << m_odoPose.x << " " << m_odoPose.y << " " <<m_odoPose.theta << endl; cerr << "New Odometry Pose (reported from observation)= " << relPose.x << " " << relPose.y << " " <<relPose.theta << endl; cerr << "***********************************************************************" << endl; cerr << "** The Odometry has a big jump here. This is probably a bug in the **" << endl; cerr << "** odometry/laser input. We continue now, but the result is probably **" << endl; cerr << "** crap or can lead to a core dump since the map doesn't fit.... C&G **" << endl; cerr << "***********************************************************************" << endl; } //更新上次位置变量 m_odoPose=relPose; bool processed=false; //当第一次,或距离角度变化足够大,或时间变化足够大 // process a scan only if the robot has traveled a given distance or a certain amount of time has elapsed if (! m_count || m_linearDistance>=m_linearThresholdDistance || m_angularDistance>=m_angularThresholdDistance || (period_ >= 0.0 && (reading.getTime() - last_update_time_) > period_)){ last_update_time_ = reading.getTime(); ...... //this is for converting the reading in a scan-matcher feedable form //装换成double数组 assert(reading.size()==m_beams); double * plainReading = new double[m_beams]; for(unsigned int i=0; i<m_beams; i++){ plainReading[i]=reading[i]; } m_infoStream << "m_count " << m_count << endl; RangeReading* reading_copy = new RangeReading(reading.size(), &(reading[0]), static_cast<const RangeSensor*>(reading.getSensor()), reading.getTime()); if (m_count>0){ //如果不是第一次,则开始扫描匹配更新 //为每个粒子进行scanMatch,计算出来每个粒子的最优位姿,同时计算改最优位姿的得分和似然 scanMatch(plainReading); if (m_outputStream.is_open()){ m_outputStream << "LASER_READING "<< reading.size() << " "; m_outputStream << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(2); for (RangeReading::const_iterator b=reading.begin(); b!=reading.end(); b++){ m_outputStream << *b << " "; } OrientedPoint p=reading.getPose(); m_outputStream << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(6); m_outputStream << p.x << " " << p.y << " " << p.theta << " " << reading.getTime()<< endl; m_outputStream << "SM_UPDATE "<< m_particles.size() << " "; for (ParticleVector::const_iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){ const OrientedPoint& pose=it->pose; m_outputStream << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(3) << pose.x << " " << pose.y << " "; m_outputStream << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(6) << pose.theta << " " << it-> weight << " "; } m_outputStream << endl; } onScanmatchUpdate(); //由于scanMatch中对粒子的权重进行了更新,那么这个时候各个粒子的轨迹上的累计权重都需要重新计算 //这个函数即更新各个粒子的轨迹上的累计权重是更新 updateTreeWeights(false); if (m_infoStream){ m_infoStream << "neff= " << m_neff << endl; } if (m_outputStream.is_open()){ m_outputStream << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(6); m_outputStream << "NEFF " << m_neff << endl; } //根据neff的大小来进行重采样,也对地图进行更新 resample(plainReading, adaptParticles, reading_copy); } else { //如果是第一次,则直接计算活动区域,注册这次扫描。因为这个时候,对机器人的位置是非常确定的,就是(0,0,0)。 m_infoStream << "Registering First Scan"<< endl; for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){ m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea(); m_matcher.computeActiveArea(it->map, it->pose, plainReading); m_matcher.registerScan(it->map, it->pose, plainReading); // cyr: not needed anymore, particles refer to the root in the beginning! TNode* node=new TNode(it->pose, 0., it->node, 0); //node->reading=0; node->reading = reading_copy; it->node=node; } } // cerr << "Tree: normalizing, resetting and propagating weights at the end..." ; //进行重采样之后,粒子的权重又会发生变化,因此需要再次更新粒子轨迹的累计权重。 updateTreeWeights(false); // cerr << ".done!" <<endl; delete [] plainReading; m_lastPartPose=m_odoPose; //update the past pose for the next iteration m_linearDistance=0; m_angularDistance=0; m_count++; processed=true; //keep ready for the next step for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){ it->previousPose=it->pose; } } if (m_outputStream.is_open()) m_outputStream << flush; m_readingCount++; return processed; } |
扫描更新
SlamGMapping::laserCallback() at slam_gmapping.cpp:628
–> SlamGMapping::addScan() at slam_gmapping.cpp:606
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::processScan() at gridslamprocessor.cpp:419
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::scanMatch() at gridslamprocessor.hxx:16
/**Just scan match every single particle. If the scan matching fails, the particle gets a default likelihood.*/ inline void GridSlamProcessor::scanMatch(const double* plainReading){ // sample a new pose from each scan in the reference double sumScore=0; //对所有粒子都利用当前的激光扫描进行位置,权重更新。 for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){ OrientedPoint corrected; double score, l, s; //对当前粒子利用当前的激光扫描进行位置计算并评分 score=m_matcher.optimize(corrected, it->map, it->pose, plainReading); // it->pose=corrected; //如果评分法大于最小得分,则更新当前粒子的位置为计算出位置 if (score>m_minimumScore){ it->pose=corrected; } else { if (m_infoStream){ m_infoStream << "Scan Matching Failed, using odometry. Likelihood=" << l <<std::endl; m_infoStream << "lp:" << m_lastPartPose.x << " " << m_lastPartPose.y << " "<< m_lastPartPose.theta <<std::endl; m_infoStream << "op:" << m_odoPose.x << " " << m_odoPose.y << " "<< m_odoPose.theta <<std::endl; } } //粒子的最优位姿计算了之后,重新计算粒子的权重(相当于粒子滤波器中的观测步骤,计算p(z|x,m)),粒子的权重由粒子的似然来表示。 //后续会根据粒子的权重进行重采样。 m_matcher.likelihoodAndScore(s, l, it->map, it->pose, plainReading); sumScore+=score; it->weight+=l; it->weightSum+=l; //set up the selective copy of the active area //by detaching the areas that will be updated m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea(); m_matcher.computeActiveArea(it->map, it->pose, plainReading); } if (m_infoStream) m_infoStream << "Average Scan Matching Score=" << sumScore/m_particles.size() << std::endl; } |
计算当前粒子的最优位置和得分
SlamGMapping::laserCallback() at slam_gmapping.cpp:628
–> SlamGMapping::addScan() at slam_gmapping.cpp:606
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::processScan() at gridslamprocessor.cpp:419
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::scanMatch() at gridslamprocessor.hxx:16
–> GMapping::ScanMatcher::optimize() at scanmatcher.cpp:340
optomize的中心思想就是给一个初始位姿结合激光数据和地图求出最优位姿。由于这个初始位姿可能不够准确,但是我们要怎么找倒较准确的位姿(最优位姿)呢?
在初始位姿的基础上,我们给他的x,y,thelta方向上依次给一个增量,计算每一次的位姿得分(得分表示在该位姿下激光束和地图的匹配程度),看看是不是比不给增量之前得分高,得分高意味着位姿更准确了。这样迭代求出最优位姿。代码流程如下:
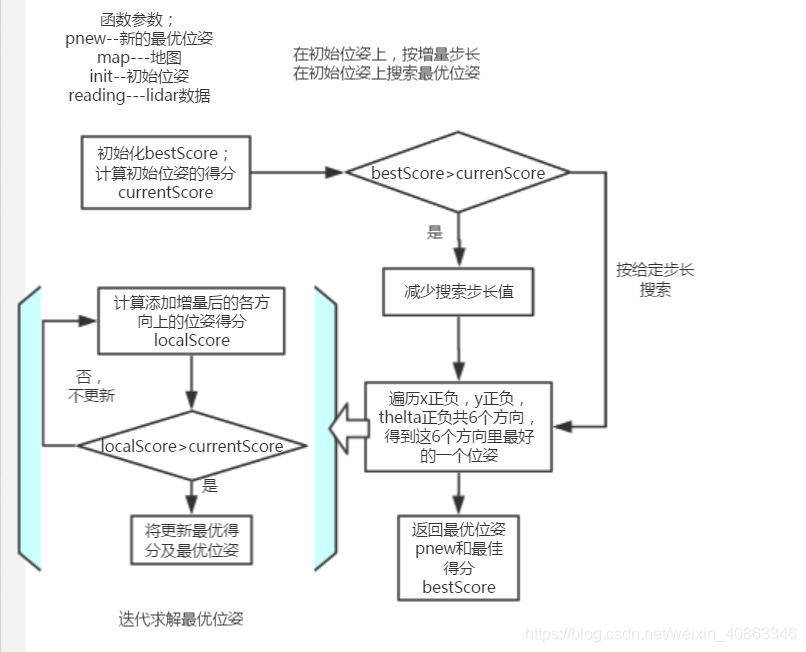
double ScanMatcher::optimize(OrientedPoint& pnew, const ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& init, const double* readings) const{ double bestScore=-1; OrientedPoint currentPose=init; //计算当前位置的得分 double currentScore=score(map, currentPose, readings); //8个方向搜索的间隔 double adelta=m_optAngularDelta, ldelta=m_optLinearDelta; unsigned int refinement=0; enum Move{Front, Back, Left, Right, TurnLeft, TurnRight, Done}; /* cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__<< " readings: "; for (int i=0; i<m_laserBeams; i++){ cout << readings[i] << " "; } cout << endl; */ int c_iterations=0; do{ if (bestScore>=currentScore){ refinement++; adelta*=.5; ldelta*=.5; } bestScore=currentScore; // cout <<"score="<< currentScore << " refinement=" << refinement; // cout << "pose=" << currentPose.x << " " << currentPose.y << " " << currentPose.theta << endl; OrientedPoint bestLocalPose=currentPose; OrientedPoint localPose=currentPose; //计算当前位置相邻的8个位置的得分和位置 Move move=Front; do { localPose=currentPose; switch(move){ case Front: localPose.x+=ldelta; move=Back; break; case Back: localPose.x-=ldelta; move=Left; break; case Left: localPose.y-=ldelta; move=Right; break; case Right: localPose.y+=ldelta; move=TurnLeft; break; case TurnLeft: localPose.theta+=adelta; move=TurnRight; break; case TurnRight: localPose.theta-=adelta; move=Done; break; default:; } double odo_gain=1; //如果对里程计比较信任,那么就要降低8个方向的增益值 if (m_angularOdometryReliability>0.){ double dth=init.theta-localPose.theta; dth=atan2(sin(dth), cos(dth)); dth*=dth; odo_gain*=exp(-m_angularOdometryReliability*dth); } if (m_linearOdometryReliability>0.){ double dx=init.x-localPose.x; double dy=init.y-localPose.y; double drho=dx*dx+dy*dy; odo_gain*=exp(-m_linearOdometryReliability*drho); } double localScore=odo_gain*score(map, localPose, readings); if (localScore>currentScore){ currentScore=localScore; bestLocalPose=localPose; } c_iterations++; } while(move!=Done); currentPose=bestLocalPose; // cout << "currentScore=" << currentScore<< endl; //here we look for the best move; }while (currentScore>bestScore || refinement<m_optRecursiveIterations); //cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "bestScore=" << bestScore<< endl; //cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "iterations=" << c_iterations<< endl; //得到粒子最新的位姿 pnew=currentPose; return bestScore; } |
计算当前粒子的其中一个位置的得分
SlamGMapping::laserCallback() at slam_gmapping.cpp:628
–> SlamGMapping::addScan() at slam_gmapping.cpp:606
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::processScan() at gridslamprocessor.cpp:419
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::scanMatch() at gridslamprocessor.hxx:16
–> GMapping::ScanMatcher::optimize() at scanmatcher.cpp:
Score方法采样的原理来自:

inline double ScanMatcher::score(const ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& p, const double* readings) const{ double s=0; //angle数组存储激光束依次的角度信息 const double * angle=m_laserAngles+m_initialBeamsSkip; //lp用于存储激光的位姿,p为粒子的位置,经过tf变换可以得到激光的位姿 OrientedPoint lp=p; lp.x+=cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x-sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y; lp.y+=sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x+cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y; lp.theta+=m_laserPose.theta; unsigned int skip=0; //存储离击中位姿多远的间距认为是自由未被占用的位姿 double freeDelta=map.getDelta()*m_freeCellRatio; //迭代所以激光束计算最优值 for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; r<readings+m_laserBeams; r++, angle++){ skip++; skip=skip>m_likelihoodSkip?0:skip; if (skip||*r>m_usableRange||*r==0.0) continue; //phit表示被击中的位姿,根据激光的位姿和激光被阻挡返回的长度计算 Point phit=lp; phit.x+=*r*cos(lp.theta+*angle); phit.y+=*r*sin(lp.theta+*angle); IntPoint iphit=map.world2map(phit); //pfree表示被击中位姿的前面的自由未被占用的位姿。被击中的前面必定是未被击中的。 Point pfree=lp; pfree.x+=(*r-map.getDelta()*freeDelta)*cos(lp.theta+*angle); pfree.y+=(*r-map.getDelta()*freeDelta)*sin(lp.theta+*angle); //这儿pfree存储为与被击中位姿的间距,ipfree表示为转换成地图坐标后的值 pfree=pfree-phit; IntPoint ipfree=map.world2map(pfree); bool found=false; //bestMu表示被击中的点与对应的cell的均值(位姿)的最短值 Point bestMu(0.,0.); for (int xx=-m_kernelSize; xx<=m_kernelSize; xx++) for (int yy=-m_kernelSize; yy<=m_kernelSize; yy++){ IntPoint pr=iphit+IntPoint(xx,yy); IntPoint pf=pr+ipfree; //AccessibilityState s=map.storage().cellState(pr); //if (s&Inside && s&Allocated){ const PointAccumulator& cell=map.cell(pr); const PointAccumulator& fcell=map.cell(pf); //被击中的cell的概率要大于m_fullnessThreshold,同时自由的fcell必须小于m_fullnessThreshold才合理。 if (((double)cell )> m_fullnessThreshold && ((double)fcell )<m_fullnessThreshold){ //mu为被击中的点与对应的cell的均值(位姿)的距离 Point mu=phit-cell.mean(); if (!found){ bestMu=mu; found=true; }else bestMu=(mu*mu)<(bestMu*bestMu)?mu:bestMu; } //} } if (found) //显然,距离越近得分越高,越表明粒子越接近于真实的激光雷达的位姿,其在参与激光雷达位姿计算时的权重越大。 s+=exp(-1./m_gaussianSigma*bestMu*bestMu); } return s; } |
其中cell的mean方法返回cell中所有点的位姿的均值。更新的时候实际是做累加运算。cell重载double()运算符,所以(double)cell返回的是被击中的概率。
inline Point mean() const {return 1./n*Point(acc.x, acc.y);} inline operator double() const { return visits?(double)n*SIGHT_INC/(double)visits:-1; } void PointAccumulator::update(bool value, const Point& p){ if (value) { acc.x+= static_cast<float>(p.x); acc.y+= static_cast<float>(p.y); n++; visits+=SIGHT_INC; } else visits++; } |
计算当前粒子的似然和得分
SlamGMapping::laserCallback() at slam_gmapping.cpp:628
–> SlamGMapping::addScan() at slam_gmapping.cpp:606
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::processScan() at gridslamprocessor.cpp:419
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::scanMatch() at gridslamprocessor.hxx:16
–> GMapping::ScanMatcher::likelihoodAndScore() at scanmatcher.h:195
likelihoodAndScore函数如下,计算原理和score函数是一样的,只不过函数里的位姿是匹配成功的最优位姿或者是(匹配不成功时)的里程计位姿;除了该粒子的得分外,还计算了该粒子的所有似然值的和,这个似然和是把没有击中障碍物的激光束也算进去了,这个似然和用来表示该粒子的权重。
inline unsigned int ScanMatcher::likelihoodAndScore(double& s, double& l, const ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& p, const double* readings) const{ using namespace std; l=0; s=0; const double * angle=m_laserAngles+m_initialBeamsSkip; OrientedPoint lp=p; lp.x+=cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x-sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y; lp.y+=sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x+cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y; lp.theta+=m_laserPose.theta; //如果没有击中的时候的似然值 nullLikehood = -0.5 double noHit=nullLikelihood/(m_likelihoodSigma); unsigned int skip=0; unsigned int c=0; double freeDelta=map.getDelta()*m_freeCellRatio; for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; r<readings+m_laserBeams; r++, angle++){ skip++; skip=skip>m_likelihoodSkip?0:skip; if (*r>m_usableRange) continue; if (skip) continue; Point phit=lp; phit.x+=*r*cos(lp.theta+*angle); phit.y+=*r*sin(lp.theta+*angle); IntPoint iphit=map.world2map(phit); Point pfree=lp; pfree.x+=(*r-freeDelta)*cos(lp.theta+*angle); pfree.y+=(*r-freeDelta)*sin(lp.theta+*angle); pfree=pfree-phit; IntPoint ipfree=map.world2map(pfree); bool found=false; Point bestMu(0.,0.); for (int xx=-m_kernelSize; xx<=m_kernelSize; xx++) for (int yy=-m_kernelSize; yy<=m_kernelSize; yy++){ IntPoint pr=iphit+IntPoint(xx,yy); IntPoint pf=pr+ipfree; //AccessibilityState s=map.storage().cellState(pr); //if (s&Inside && s&Allocated){ const PointAccumulator& cell=map.cell(pr); const PointAccumulator& fcell=map.cell(pf); //被击中的cell的概率要大于m_fullnessThreshold,同时自由的fcell必须小于m_fullnessThreshold才合理。 if (((double)cell )>m_fullnessThreshold && ((double)fcell )<m_fullnessThreshold){ Point mu=phit-cell.mean(); if (!found){ bestMu=mu; found=true; }else bestMu=(mu*mu)<(bestMu*bestMu)?mu:bestMu; } //} } if (found){ s+=exp(-1./m_gaussianSigma*bestMu*bestMu); c++; } if (!skip){ //似然不是指数,似然只是指数的上标,距离越小,似然度越大。 double f=(-1./m_likelihoodSigma)*(bestMu*bestMu); l+=(found)?f:noHit; } } return c; } |
计算当前粒子的活动区域
SlamGMapping::laserCallback() at slam_gmapping.cpp:628
–> SlamGMapping::addScan() at slam_gmapping.cpp:606
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::processScan() at gridslamprocessor.cpp:419
–> GMapping::GridSlamProcessor::scanMatch() at gridslamprocessor.hxx:16
–> GMapping::ScanMatcher::computeActiveArea() at scanmatcher.cpp:119
void ScanMatcher::computeActiveArea(ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& p, const double* readings){ if (m_activeAreaComputed) return; //激光雷达的位姿lp OrientedPoint lp=p; lp.x+=cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x-sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y; lp.y+=sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x+cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y; lp.theta+=m_laserPose.theta; IntPoint p0=map.world2map(lp); //地图的最小点和最大点 Point min(map.map2world(0,0)); Point max(map.map2world(map.getMapSizeX()-1,map.getMapSizeY()-1)); //扩展地图到覆盖lp if (lp.x<min.x) min.x=lp.x; if (lp.y<min.y) min.y=lp.y; if (lp.x>max.x) max.x=lp.x; if (lp.y>max.y) max.y=lp.y; /*determine the size of the area*/ //扩展地图到覆盖所有的激光束hit点 const double * angle=m_laserAngles+m_initialBeamsSkip; for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; r<readings+m_laserBeams; r++, angle++){ if (*r>m_laserMaxRange||*r==0.0||isnan(*r)) continue; double d=*r>m_usableRange?m_usableRange:*r; Point phit=lp; phit.x+=d*cos(lp.theta+*angle); phit.y+=d*sin(lp.theta+*angle); if (phit.x<min.x) min.x=phit.x; if (phit.y<min.y) min.y=phit.y; if (phit.x>max.x) max.x=phit.x; if (phit.y>max.y) max.y=phit.y; } //min=min-Point(map.getDelta(),map.getDelta()); //max=max+Point(map.getDelta(),map.getDelta()); //膨胀map到min和max的范围 if ( !map.isInside(min) || !map.isInside(max)){ Point lmin(map.map2world(0,0)); Point lmax(map.map2world(map.getMapSizeX()-1,map.getMapSizeY()-1)); //cerr << "CURRENT MAP " << lmin.x << " " << lmin.y << " " << lmax.x << " " << lmax.y << endl; //cerr << "BOUNDARY OVERRIDE " << min.x << " " << min.y << " " << max.x << " " << max.y << endl; min.x=( min.x >= lmin.x )? lmin.x: min.x-m_enlargeStep; max.x=( max.x <= lmax.x )? lmax.x: max.x+m_enlargeStep; min.y=( min.y >= lmin.y )? lmin.y: min.y-m_enlargeStep; max.y=( max.y <= lmax.y )? lmax.y: max.y+m_enlargeStep; map.resize(min.x, min.y, max.x, max.y); //cerr << "RESIZE " << min.x << " " << min.y << " " << max.x << " " << max.y << endl; } HierarchicalArray2D<PointAccumulator>::PointSet activeArea; /*allocate the active area*/ angle=m_laserAngles+m_initialBeamsSkip; for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; r<readings+m_laserBeams; r++, angle++) if (m_generateMap){ double d=*r; if (d>m_laserMaxRange||d==0.0||isnan(d)) continue; if (d>m_usableRange) d=m_usableRange; Point phit=lp+Point(d*cos(lp.theta+*angle),d*sin(lp.theta+*angle)); IntPoint p0=map.world2map(lp); IntPoint p1=map.world2map(phit); //IntPoint linePoints[20000] ; GridLineTraversalLine line; line.points=m_linePoints; GridLineTraversal::gridLine(p0, p1, &line); for (int i=0; i<line.num_points-1; i++){ assert(map.isInside(m_linePoints[i])); activeArea.insert(map.storage().patchIndexes(m_linePoints[i])); assert(m_linePoints[i].x>=0 && m_linePoints[i].y>=0); } if (d<m_usableRange){ IntPoint cp=map.storage().patchIndexes(p1); assert(cp.x>=0 && cp.y>=0); activeArea.insert(cp); } } else { if (*r>m_laserMaxRange||*r>m_usableRange||*r==0.0||isnan(*r)) continue; Point phit=lp; phit.x+=*r*cos(lp.theta+*angle); phit.y+=*r*sin(lp.theta+*angle); IntPoint p1=map.world2map(phit); assert(p1.x>=0 && p1.y>=0); IntPoint cp=map.storage().patchIndexes(p1); assert(cp.x>=0 && cp.y>=0); activeArea.insert(cp); } //this allocates the unallocated cells in the active area of the map //cout << "activeArea::size() " << activeArea.size() << endl; /* cerr << "ActiveArea="; for (HierarchicalArray2D<PointAccumulator>::PointSet::const_iterator it=activeArea.begin(); it!= activeArea.end(); it++){ cerr << "(" << it->x <<"," << it->y << ") "; } cerr << endl; */ map.storage().setActiveArea(activeArea, true); m_activeAreaComputed=true; } |
更新所有粒子的权重
//BEGIN void GridSlamProcessor::updateTreeWeights(bool weightsAlreadyNormalized){ if (!weightsAlreadyNormalized) { normalize(); } resetTree(); propagateWeights(); } void GridSlamProcessor::resetTree(){ // don't calls this function directly, use updateTreeWeights(..) ! for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){ TNode* n=it->node; while (n){ n->accWeight=0; n->visitCounter=0; n=n->parent; } } } double propagateWeight(GridSlamProcessor::TNode* n, double weight){ if (!n) return weight; double w=0; n->visitCounter++; n->accWeight+=weight; if (n->visitCounter==n->childs){ w=propagateWeight(n->parent,n->accWeight); } assert(n->visitCounter<=n->childs); return w; } double GridSlamProcessor::propagateWeights(){ // don't calls this function directly, use updateTreeWeights(..) ! // all nodes must be resetted to zero and weights normalized //求所有根节点的累计权重之和 // the accumulated weight of the root double lastNodeWeight=0; //求所有叶子节点的累计权重之和 // sum of the weights in the leafs double aw=0; std::vector<double>::iterator w=m_weights.begin(); for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){ //求解所有叶子节点的累计权重 double weight=*w; aw+=weight; //叶子节点的子节点累计权重就等于自己的权重 因为它没有子节点 //每一个粒子的路径都是从叶子节点开始的,得到了叶子节点,就得到了路径 TNode * n=it->node; n->accWeight=weight; lastNodeWeight+=propagateWeight(n->parent,n->accWeight); w++; } if (fabs(aw-1.0) > 0.0001 || fabs(lastNodeWeight-1.0) > 0.0001) { cerr << "ERROR: "; cerr << "root->accWeight=" << lastNodeWeight << " sum_leaf_weights=" << aw << endl; assert(0); } return lastNodeWeight; } }; //END |
对所有粒子重采样
inline bool GridSlamProcessor::resample(const double* plainReading, int adaptSize, const RangeReading* reading){ bool hasResampled = false; TNodeVector oldGeneration; for (unsigned int i=0; i<m_particles.size(); i++){ oldGeneration.push_back(m_particles[i].node); } if (m_neff<m_resampleThreshold*m_particles.size()){ if (m_infoStream) m_infoStream << "*************RESAMPLE***************" << std::endl; uniform_resampler<double, double> resampler; m_indexes=resampler.resampleIndexes(m_weights, adaptSize); if (m_outputStream.is_open()){ m_outputStream << "RESAMPLE "<< m_indexes.size() << " "; for (std::vector<unsigned int>::const_iterator it=m_indexes.begin(); it!=m_indexes.end(); it++){ m_outputStream << *it << " "; } m_outputStream << std::endl; } onResampleUpdate(); //BEGIN: BUILDING TREE ParticleVector temp; unsigned int j=0; std::vector<unsigned int> deletedParticles; //this is for deleteing the particles which have been resampled away. // cerr << "Existing Nodes:" ; for (unsigned int i=0; i<m_indexes.size(); i++){ // cerr << " " << m_indexes[i]; while(j<m_indexes[i]){ deletedParticles.push_back(j); j++; } if (j==m_indexes[i]) j++; Particle & p=m_particles[m_indexes[i]]; TNode* node=0; TNode* oldNode=oldGeneration[m_indexes[i]]; // cerr << i << "->" << m_indexes[i] << "B("<<oldNode->childs <<") "; node=new TNode(p.pose, 0, oldNode, 0); //node->reading=0; node->reading=reading; // cerr << "A("<<node->parent->childs <<") " <<endl; temp.push_back(p); temp.back().node=node; temp.back().previousIndex=m_indexes[i]; } while(j<m_indexes.size()){ deletedParticles.push_back(j); j++; } // cerr << endl; std::cerr << "Deleting Nodes:"; for (unsigned int i=0; i<deletedParticles.size(); i++){ std::cerr <<" " << deletedParticles[i]; delete m_particles[deletedParticles[i]].node; m_particles[deletedParticles[i]].node=0; } std::cerr << " Done" <<std::endl; //END: BUILDING TREE std::cerr << "Deleting old particles..." ; m_particles.clear(); std::cerr << "Done" << std::endl; std::cerr << "Copying Particles and Registering scans..."; for (ParticleVector::iterator it=temp.begin(); it!=temp.end(); it++){ it->setWeight(0); m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea(); m_matcher.registerScan(it->map, it->pose, plainReading); m_particles.push_back(*it); } std::cerr << " Done" <<std::endl; hasResampled = true; } else { int index=0; std::cerr << "Registering Scans:"; TNodeVector::iterator node_it=oldGeneration.begin(); for (ParticleVector::iterator it=m_particles.begin(); it!=m_particles.end(); it++){ //create a new node in the particle tree and add it to the old tree //BEGIN: BUILDING TREE TNode* node=0; node=new TNode(it->pose, 0.0, *node_it, 0); //node->reading=0; node->reading=reading; it->node=node; //END: BUILDING TREE m_matcher.invalidateActiveArea(); m_matcher.registerScan(it->map, it->pose, plainReading); it->previousIndex=index; index++; node_it++; } std::cerr << "Done" <<std::endl; } //END: BUILDING TREE return hasResampled; } |
double ScanMatcher::registerScan(ScanMatcherMap& map, const OrientedPoint& p, const double* readings){ if (!m_activeAreaComputed) computeActiveArea(map, p, readings); //this operation replicates the cells that will be changed in the registration operation map.storage().allocActiveArea(); OrientedPoint lp=p; lp.x+=cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x-sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y; lp.y+=sin(p.theta)*m_laserPose.x+cos(p.theta)*m_laserPose.y; lp.theta+=m_laserPose.theta; IntPoint p0=map.world2map(lp); const double * angle=m_laserAngles+m_initialBeamsSkip; double esum=0; for (const double* r=readings+m_initialBeamsSkip; r<readings+m_laserBeams; r++, angle++) if (m_generateMap){ double d=*r; if (d>m_laserMaxRange||d==0.0||isnan(d)) continue; if (d>m_usableRange) d=m_usableRange; Point phit=lp+Point(d*cos(lp.theta+*angle),d*sin(lp.theta+*angle)); IntPoint p1=map.world2map(phit); //IntPoint linePoints[20000] ; GridLineTraversalLine line; line.points=m_linePoints; GridLineTraversal::gridLine(p0, p1, &line); for (int i=0; i<line.num_points-1; i++){ PointAccumulator& cell=map.cell(line.points[i]); double e=-cell.entropy(); cell.update(false, Point(0,0)); e+=cell.entropy(); esum+=e; } if (d<m_usableRange){ double e=-map.cell(p1).entropy(); map.cell(p1).update(true, phit); e+=map.cell(p1).entropy(); esum+=e; } } else { if (*r>m_laserMaxRange||*r>m_usableRange||*r==0.0||isnan(*r)) continue; Point phit=lp; phit.x+=*r*cos(lp.theta+*angle); phit.y+=*r*sin(lp.theta+*angle); IntPoint p1=map.world2map(phit); assert(p1.x>=0 && p1.y>=0); map.cell(p1).update(true,phit); } //cout << "informationGain=" << -esum << endl; return esum; } |
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40863346/article/details/102562781
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40863346/article/details/88870663本作品采用知识共享署名 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。